Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2009
Laser radiation 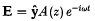 propagating through a non-uniform plasma along the direction of the density gradient suffers total reflection at the critical layer. However, when a wiggler magnetic field
propagating through a non-uniform plasma along the direction of the density gradient suffers total reflection at the critical layer. However, when a wiggler magnetic field 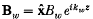 exists near the critical layer, the laser drives a Langmuir wave. For suitable values of Bw and kw, the power transfer from the laser to the Langmuir wave could be as high as 60%. The Langmuir wave deposits its energy on the electrons via Landau damping. This may be an efficient mechanism of laser absorption when large self-generated magnetic fields exist in the plasma.
exists near the critical layer, the laser drives a Langmuir wave. For suitable values of Bw and kw, the power transfer from the laser to the Langmuir wave could be as high as 60%. The Langmuir wave deposits its energy on the electrons via Landau damping. This may be an efficient mechanism of laser absorption when large self-generated magnetic fields exist in the plasma.