Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2009
An inhomogeneous plasma column surrounded by a glass wall is described through full first order in temperatures Te and Ti using a complete electromagnetic treatment. We study the response of this system to a purely TE wave with K perpendicular to the axis. Comparison with existing theories and experimental results is made in the electron–wave domain (ions play no role) with zero steady magnetic field, i.e. in the case of temperature (Tonks-Dattner) resonances. Perhaps surprising at first sight, there is poor agreement with experiment at low density, the classic T½e theory (scalar perturbed pressure approximation) giving far better results. Simple arguments concerning the different levels of approximation in the description of the longitudinal k2 enable us to distinguish the crucial difference existing between a scalar pressure and a complete T description and to understand this result. We generalize these findings, demoastrating that a 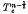 description is always more realistic than a
description is always more realistic than a 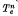 one in the range ωpe<ω.
one in the range ωpe<ω.