Article contents
Transverse instability of electron phase-space holes in multi-dimensional Maxwellian plasmas
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 November 2018
Abstract
The stability of an initially one-dimensional electron hole to perturbations varying sinusoidally transverse to its trapping direction is analysed in detail. It is shown that the expected low-frequency eigenmode of the linearized Vlasov–Poisson system consists of a shift mode, proportional to the gradient of the equilibrium potential. The resulting dispersion relation is that the total jetting force exerted by a perturbed hole on the particles balances the electric restoring tension of the hole. The tension is quantitatively small and can often be ignored. The particle force is expressed as integrals of equilibrium parameters over the hole and is shown at low frequency to be exactly equal to what has recently been found (by different analysis) to express ‘kinematic’ hole momentum conservation. The mechanism of instability has nothing to do with the previously hypothesized transverse electron focusing. The unmagnetized growth rate 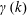 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}(k)$ is found numerically and is in excellent agreement with recent kinematic estimates. Magnetic field stabilization of the transverse mode is also evaluated. The resulting stability boundary for Maxwellian holes is in reasonable agreement with previously published criteria based on particle simulation. It arises from a change of trapped force sign across the resonance between bounce and cyclotron frequencies.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}(k)$ is found numerically and is in excellent agreement with recent kinematic estimates. Magnetic field stabilization of the transverse mode is also evaluated. The resulting stability boundary for Maxwellian holes is in reasonable agreement with previously published criteria based on particle simulation. It arises from a change of trapped force sign across the resonance between bounce and cyclotron frequencies.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2018
References
- 12
- Cited by


