Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Hager, R.
Dominski, J.
and
Chang, C. S.
2019.
Cross-verification of neoclassical transport solutions from XGCa against NEO.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 10,
Maget, Patrick
Manas, Pierre
Frank, Judith
Nicolas, Timothée
Agullo, Olivier
and
Garbet, Xavier
2020.
An analytic model for the collisional transport and poloidal asymmetry distribution of impurities in tokamak plasmas.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 10,
p.
105001.
MORITAKA, Toseo
COLE, Michael
HAGER, Robert
KU, Seung-Hoe
CHANG, C. S.
and
ISHIGURO, Seiji
2021.
Improving Gyrokinetic Field Solvers toward Whole-Volume Modeling of Stellarators.
Plasma and Fusion Research,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 0,
p.
2403054.
Miller, M. A.
Churchill, R. M.
Dener, A.
Chang, C. S.
Munson, T.
and
Hager, R.
2021.
Encoder–decoder neural network for solving the nonlinear Fokker–Planck–Landau collision operator in XGC.
Journal of Plasma Physics,
Vol. 87,
Issue. 2,
Angioni, Clemente
2021.
Impurity transport in tokamak plasmas, theory, modelling and comparison with experiments .
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion,
Vol. 63,
Issue. 7,
p.
073001.
Sharma, A. Y.
Cole, M. D. J.
Görler, T.
Chen, Y.
Hatch, D. R.
Guttenfelder, W.
Hager, R.
Sturdevant, B. J.
Ku, S.
Mishchenko, A.
and
Chang, C. S.
2022.
Global gyrokinetic study of shaping effects on electromagnetic modes at NSTX aspect ratio with ad hoc parallel magnetic perturbation effects.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 11,
Trivedi, P.
Dominski, J.
Chang, C. S.
and
Ku, S.
2022.
Toward the core-edge coupling of delta-f and total-f gyrokinetic models.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 3,
Hager, Robert
Ku, S.
Sharma, A. Y.
Chang, C. S.
Churchill, R. M.
and
Scheinberg, A.
2022.
Electromagnetic total-f algorithm for gyrokinetic particle-in-cell simulations of boundary plasma in XGC.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 11,
Lim, K.
Garbet, X.
Sarazin, Y.
Gravier, E.
Lesur, M.
Lo-Cascio, G.
and
Rouyer, T.
2023.
Self-consistent gyrokinetic modeling of turbulent and neoclassical tungsten transport in toroidally rotating plasmas.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 8,
Dominski, J.
Chang, C. S.
Hager, R.
Ku, S.
Yoon, E. S.
and
Parail, V.
2024.
Neoclassical transport of tungsten ion bundles in total-f neoclassical gyrokinetic simulations of a whole-volume JET-like plasma.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 3,
Trivedi, P.
Dominski, J.
Chang, C. S.
Ku, S.
and
Scheinberg, A.
2024.
Core-edge modeling of gyrokinetic turbulence by coupling the delta-f and total-f models in the XGC code.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 7,
Dominski, J.
Maget, P.
Manas, P.
Morales, J.
Ku, S.
Scheinberg, A.
Chang, C.S.
Hager, R.
and
O’Mullane, M.
2025.
Gyrokinetic prediction of core tungsten peaking in a WEST plasma with nitrogen impurities.
Nuclear Fusion,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 1,
p.
016003.
Bottino, A
Stier, A
Boesl, M
Hayward-Schneider, T
Bergmann, A
Coster, D
Brunner, S
Giannatale, G Di
and
Villard, L
2025.
Particle-in-cell methods in edge plasma physics: the PICLS code.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion,
Vol. 67,
Issue. 2,
p.
025008.
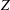 $Z$ impurities with the new impurity version of XGCa
$Z$ impurities with the new impurity version of XGCa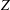 $Z$ impurity particles in the Pfirsch–Schlüter regime can exhibit a significant level of up–down poloidal asymmetry, through the large parallel friction force, and thus influence the radial plasma transport significantly. The study is performed in a plasma with weak toroidal rotation. In comparison, when the impurity particles are in the plateau regime, the up–down poloidal asymmetry becomes weak, with the parallel friction force becoming weaker than the parallel viscous force. It is also found that the linearization of the perturbed distribution function, based on the small poloidal asymmetry assumption, can become invalid. Using the numerical data from XGCa, each term in the parallel fluid force-balance equation have been analysed to find that both the main ions and the electrons respond to the poloidal potential variation adiabatically when the high-
$Z$ impurity particles in the Pfirsch–Schlüter regime can exhibit a significant level of up–down poloidal asymmetry, through the large parallel friction force, and thus influence the radial plasma transport significantly. The study is performed in a plasma with weak toroidal rotation. In comparison, when the impurity particles are in the plateau regime, the up–down poloidal asymmetry becomes weak, with the parallel friction force becoming weaker than the parallel viscous force. It is also found that the linearization of the perturbed distribution function, based on the small poloidal asymmetry assumption, can become invalid. Using the numerical data from XGCa, each term in the parallel fluid force-balance equation have been analysed to find that both the main ions and the electrons respond to the poloidal potential variation adiabatically when the high- $Z$ tungsten possesses large poloidal variation.
$Z$ tungsten possesses large poloidal variation.