Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 November 2022
We investigate three-dimensional (3-D) bow shocks in a highly collisional magnetized aluminium plasma, generated during the ablation phase of an exploding wire array on the MAGPIE facility (1.4 MA, 240 ns). Ablation of plasma from the wire array generates radially diverging, supersonic ($M_S \sim 7$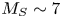 ), super-Alfvénic ($M_A > 1$
), super-Alfvénic ($M_A > 1$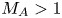 ) magnetized flows with frozen-in magnetic flux ($R_M \gg 1$
) magnetized flows with frozen-in magnetic flux ($R_M \gg 1$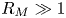 ). These flows collide with an inductive probe placed in the flow, which serves both as the obstacle that generates the magnetized bow shock, and as a diagnostic of the advected magnetic field. Laser interferometry along two orthogonal lines of sight is used to measure the line-integrated electron density. A detached bow shock forms ahead of the probe, with a larger opening angle in the plane parallel to the magnetic field than in the plane normal to it. Since the resistive diffusion length of the plasma is comparable to the probe size, the magnetic field decouples from the ion fluid at the shock front and generates a hydrodynamic shock, whose structure is determined by the sonic Mach number, rather than the magnetosonic Mach number of the flow. The 3-D simulations performed using the resistive magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) code Gorgon confirm this picture, but under-predict the anisotropy observed in the shape of the experimental bow shock, suggesting that non-MHD mechanisms may be important for modifying the shock structure.
). These flows collide with an inductive probe placed in the flow, which serves both as the obstacle that generates the magnetized bow shock, and as a diagnostic of the advected magnetic field. Laser interferometry along two orthogonal lines of sight is used to measure the line-integrated electron density. A detached bow shock forms ahead of the probe, with a larger opening angle in the plane parallel to the magnetic field than in the plane normal to it. Since the resistive diffusion length of the plasma is comparable to the probe size, the magnetic field decouples from the ion fluid at the shock front and generates a hydrodynamic shock, whose structure is determined by the sonic Mach number, rather than the magnetosonic Mach number of the flow. The 3-D simulations performed using the resistive magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) code Gorgon confirm this picture, but under-predict the anisotropy observed in the shape of the experimental bow shock, suggesting that non-MHD mechanisms may be important for modifying the shock structure.