Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 December 2020
The paper analyses the penetration of a magnetic field into the plasma bridge of nanosecond and microsecond opening switches. For switches with a conduction time of ~100 ns, simple formulae are derived to estimate the magnetic field velocity in collisionless and collisional plasmas. It is shown that in both cases this velocity is determined by the magnetic field rise rate to plasma density ratio raised to the power of 1/2. As the conduction time is increased to ~1 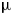 ${\rm \mu}$s, the field velocity starts to depend on the plasma aggregation by a magnetic piston. At the same time, irrespective of the conduction time, the electron flow velocity is limited by the radial drift velocity in crossed magnetic and polarization electric fields. Such a limitation suppresses the current channel conductivity with respect to the Spitzer value by a factor equal to the electron magnetization parameter raised to one or another power. On completion of the conduction phase, the rate of rise of the switch resistance is proportional to the electron drift velocity. The peak switch voltage obtained in calculations is compared with its values recorded in experiments on mega-ampere current switching. A procedure is also presented for calculating the switch parameters to obtain the maximum possible voltage in the phase of current cutoff.
${\rm \mu}$s, the field velocity starts to depend on the plasma aggregation by a magnetic piston. At the same time, irrespective of the conduction time, the electron flow velocity is limited by the radial drift velocity in crossed magnetic and polarization electric fields. Such a limitation suppresses the current channel conductivity with respect to the Spitzer value by a factor equal to the electron magnetization parameter raised to one or another power. On completion of the conduction phase, the rate of rise of the switch resistance is proportional to the electron drift velocity. The peak switch voltage obtained in calculations is compared with its values recorded in experiments on mega-ampere current switching. A procedure is also presented for calculating the switch parameters to obtain the maximum possible voltage in the phase of current cutoff.