Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 August 2018
An analytic theory is presented of magnetic structures in collisionless, high-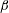 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$ plasmas. Using a reduced magnetohydrodynamic model, a stationary nonlinear solution is constructed in the form of a Kelvin–Stuart cat’s eyes chain of magnetic islands, on the spatial scale that exceeds the characteristic ion lengths. The solution is imbedded in a background current sheet and possesses both a significant plasma density perturbation trapped inside the magnetic islands and a compressional magnetic field component that is driven mostly by a current loop located at the separatrix of the islands. This theory may provide an explanation for the magnetic structures observed in the solar wind close to the Earth by the Cluster spacecraft.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$ plasmas. Using a reduced magnetohydrodynamic model, a stationary nonlinear solution is constructed in the form of a Kelvin–Stuart cat’s eyes chain of magnetic islands, on the spatial scale that exceeds the characteristic ion lengths. The solution is imbedded in a background current sheet and possesses both a significant plasma density perturbation trapped inside the magnetic islands and a compressional magnetic field component that is driven mostly by a current loop located at the separatrix of the islands. This theory may provide an explanation for the magnetic structures observed in the solar wind close to the Earth by the Cluster spacecraft.