Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2009
The quasi-linear theory of plasma waves in a collisionless plasma in the absence of external fields is formulated in a similar way to that given by Bernstein & Engelmann (1966) but is applied to the case when unstable essentially transverse electromagnetic waves with phase velocities of the order of the r.m.s. electron velocity are present. It is deduced that the wave energy reaches a maximum and then decays leaving the plasma stable. A quantitative description of the time development of a plasma with a slightly spheroidal velocity distribution is given in terms of a parameter x characterizing the anisotropy and it is found that this quantity decays exponentially as the waves grow and ultimately decays like t−β with 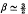 , and correspondingly the space-averaged field energy grows to a maximum and then decays like t−β.
, and correspondingly the space-averaged field energy grows to a maximum and then decays like t−β.