Article contents
Numerical investigation of a plasma beam entering transverse magnetic fields
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2009
Abstract
We study plasma-beam injection into transverse magnetic fields using both electrostatic and electromagnetic particle-in-cell (PIC) codes. In the case of small beam momentum or energy (low drift kinetic β) we study both large- and small-ion-gyroradius beams. Large-ion-gyroradius beams with a large dielectric constant ε ≫ (M/m)½ are found to propagate across the magnetic field via E × B drifts at nearly the initial injection velocity, where 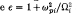 and M/m is the ion-to-electron mass ratio. Beam degradation and undulations are observed, in agreement with previous experimental and analytical results. When ε is of order (M/m)½ the plasma beam propagates across field lines at only half its initial velocity and loses its coherent structure. When ε is much less than (M/m)½ the beam particles decouple at the magnetic field boundary, scattering the electrons and slightly deflecting the ions. For small-ion-gyroradius beam injection a flute-type instability is observed at the beam-magnetic-field interface. In the case of large beam momentum or energy (high drift kinetic β) we observe good penetration of a plasma beam by shielding the magnetic field from the interior of the beam (diamagnetism). However, we observe anomalously fast penetration of the magnetic field into the beam and find that the diffusion rate depends on the electron gyroradius of the beam.
and M/m is the ion-to-electron mass ratio. Beam degradation and undulations are observed, in agreement with previous experimental and analytical results. When ε is of order (M/m)½ the plasma beam propagates across field lines at only half its initial velocity and loses its coherent structure. When ε is much less than (M/m)½ the beam particles decouple at the magnetic field boundary, scattering the electrons and slightly deflecting the ions. For small-ion-gyroradius beam injection a flute-type instability is observed at the beam-magnetic-field interface. In the case of large beam momentum or energy (high drift kinetic β) we observe good penetration of a plasma beam by shielding the magnetic field from the interior of the beam (diamagnetism). However, we observe anomalously fast penetration of the magnetic field into the beam and find that the diffusion rate depends on the electron gyroradius of the beam.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 1989
References
REFERENCES
- 11
- Cited by


