Adolescence is a period of great physical, cognitive, emotional, and social transitions that put many youths at risk of adjustment difficulties (Steinberg, Reference Steinberg2017). During this critical stage of life young people prepare to enter adulthood and play more independent roles. Experiences during adolescence can have lasting psychological, social, and economic consequences. Whether these outcomes are predominantly positive or negative is likely to depend on the interaction of multiple protective and risk factors
Immigration is an event that can have considerable impact at any stage of life (Berry, Reference Berry1997; Stevens & Vollebergh, Reference Stevens and Vollebergh2008; Vinokurov, Trickett, & Birman, Reference Vinokurov, Trickett and Birman2002). This may be especially true during adolescence, when the challenges of adapting to a new language, culture, and social milieu may exacerbate normative developmental transitions and challenges (Derluyn, Broekaert, & Schuyten, Reference Derluyn, Broekaert and Schuyten2008). Yet the wellbeing of migrant adolescents has received surprisingly little research attention worldwide, including in Pacific Rim nations (Chun & Mobley, Reference Chun and Mobley2014; Cristini, Scacchi, Perkins, Bless, & Vieno, Reference Cristini, Scacchi, Perkins, Bless and Vieno2015; c.f. Khawaja, Yang, & Cockshaw, Reference Khawaja, Yang and Cockshaw2016). Given the prevalence of immigration and the likely strength and complexity of its impacts, there is a need to investigate the ways in which immigration experiences intersect with other developmental risk and protective factors to shape adolescent adjustment.
This study assessed levels of two adjustment variables, wellbeing and depressive symptoms, in migrant adolescents and same-aged native youths. Also investigated were relationships between adolescent adjustment and four psychosocial resources, or protective factors (ethnic identity, parental support, peer support, and sense of school membership). Particular interest lay in the role of country of birth (nativity) in possibly moderating the effects of these resources on adolescent adjustment.
The Wellbeing of Migrant Adolescents
Findings from studies of the relationship between nativity and adolescent wellbeing are contradictory. While some studies (e.g., Alati, Najman, Shuttlewood, Williams, & Bor, Reference Alati, Najman, Shuttlewood, Williams and Bor2003) report no differences in the mental health of migrant and non-migrant youth, much of the research, particularly the earlier research, suggested that migrant youths are at a greater risk of distress and maladjustment (Harrison, Wilson, Pine, Chan, & Buriel, Reference Harrison, Wilson, Pine, Chan and Buriel1990; Hicks, Lalonde, & Pepler, Reference Hicks, Lalonde and Pepler1993; James, Reference James1997; Shoshami, Nakash, Zubida, & Harper, Reference Shoshami, Nakash, Zubida and Harper2016). This migrant morbidity effect has been attributed to many factors.
First, the poorer adjustment of migrant adolescents may be due to events that occurred prior to their immigration, especially in the case of economic and/or political refugees who may have suffered extreme poverty, persecution, death of loved ones, or similar traumatic events (Correa-Velez, Gifford, & Barnett, Reference Correa-Velez, Gifford and Barnett2010; Derluyn et al., Reference Derluyn, Broekaert and Schuyten2008). Second, immigration itself is a stressful process, typically associated with grief, loss of family and friends, and cultural changes (Hicks et al., Reference Hicks, Lalonde and Pepler1993; James, Reference James1997), and these diverse demands may increase the vulnerability and emotional distress of migrant children (Pawliuk et al., Reference Pawliuk, Grizenko, Chan-Yip, Gantous, Mathew and Nguyen1996).
Third, migrant children and their parents experience acculturation at different speeds, with children generally going through the process faster than do their parents. As a result, migrant families can experience more intergenerational conflict than do native families, with the extent of the acculturative demands and conflicts likely to increase as differences between migrants’ native and host cultures increase (Sluzki, Reference Sluzki1979). Fourth, a range of extra-familial, post-immigration factors can contribute to poorer mental health. As members of minority groups, with cultural and/or linguistic backgrounds different from those that prevail in their host country, migrants may encounter rejection, discrimination, and hostility from native members of the host nation (James, Reference James1997).
While these factors suggest that migrant youths should display relatively low levels of wellbeing, several studies have found the opposite (Cristini et al., Reference Cristini, Scacchi, Perkins, Bless and Vieno2015; Harker, Reference Harker2001; Harris, Reference Harris and Hernandez1999; Vaage et al., Reference Vaage, Tingvold, Hauff, Van Ta, Wentzel-Larsen, Clench-Aas and Thomsen2009). Terms such as the healthy migrant effect, and the immigrant paradox phenomenon (e.g., Bowe, Reference Bowe2017; Fuligni, Reference Fuligni1998; Marks, Ejesi, & Garcia Coll, Reference Marks, Ejesi and Garcia Coll2014), have been coined to capture this effect. There are many possible explanations. One account is built around the operation of strict processes of preimmigration selection, and consequent high levels of parental skills and qualifications. Migrating parents often have close relationships with, and high aspirations for, their children, and they tend to closely supervise their children's studies and general behaviour (Fuligni, Reference Fuligni1998; Harker, Reference Harker2001). Moreover, Trueba (Reference Trueba2002) argued that migrant children become able to switch between their identities, languages, and cultural norms to meet social expectations, and this may increase their resilience and promote mental health. Others have highlighted the strength in many migrant communities of cultural and extended family networks that provide social support when needed.
In sum, the literature suggests that both the ‘migrant morbidity’ and the ‘healthy migrant’ hypotheses may be true in some cases, for different reasons. Which effect prevails likely depends on a range of individual, ethnic group, and contextual factors, including the migrants’ economic and cultural capital, and duration of residence in the host nation (Bellmore, Witkow, Graham, & Juvonen, Reference Bellmore, Witkow, Graham and Juvonen2004; Berry, Reference Berry1997; Motti-Stafandi et al., Reference Motti-Stafandi, Pavlopoulos, Obradovic, Dalla, Takis, Papathanassiou and Masten2008; Schmitt-Rodermund & Silbereisen, Reference Schmitt-Rodermund and Silbereisen2008). The direction of the effect also varies with the criterion under study. Derluyn et al. (Reference Derluyn, Broekaert and Schuyten2008), for example, reported higher levels of peer problems but fewer anxiety symptoms in migrant than in native Belgian adolescents, while the two groups did not differ in depression. In general, the research favours a healthy migrant effect when predicting school grades, physical health, and risk-taking behaviours, but less strongly supports a positive effect on psychological adjustment (Harris, Reference Harris and Hernandez1999; Kao, Reference Kao and Hernandez1999; Motti-Stafandi et al., Reference Motti-Stafandi, Pavlopoulos, Obradovic, Dalla, Takis, Papathanassiou and Masten2008).
Any disadvantages associated with immigration are likely to be less pronounced among individuals born in countries that are culturally and linguistically similar to the host nation than among those from different cultural and linguistic backgrounds (Harris, Reference Harris and Hernandez1999; Schmitt-Rodermund & Silbereisen, Reference Schmitt-Rodermund and Silbereisen2008). In support, U.S. research shows that youths whose home language is not English have lower levels of self-esteem and self-efficacy than do migrants from English-speaking nations (Kao, Reference Kao and Hernandez1999), migrant youth who speak a language other than English (or Spanish) at home have lower levels of positive wellbeing (Harker, Reference Harker2001), and migrants who have language difficulties report greater distress (Vinokurov et al., Reference Vinokurov, Trickett and Birman2002; see also Khawaja et al., Reference Khawaja, Yang and Cockshaw2016).
The current study examined the extent to which adjustment outcomes differ between adolescents born in (a) the host nation, (b) countries that share the same first or official language as the host nation, and (c) countries in which another language predominates. This trichotomous language background variable serves as a rough proxy for the magnitude of the differences between birth and host cultures, with the assumption that the acculturation process may take longer, be more complex, and have the potential for greater distress for migrants from language and cultural backgrounds different from their adopted nation. Stronger migrant morbidity effects are thus likely to be found among migrants from backgrounds different from, rather than similar to, the host nation.
Psychosocial Resources
Our research investigated the contribution to adolescent adjustment of four psychosocial resources or protective factors: ethnic identity, parental support, peer support, and sense of school membership. As detailed below, we conceptualised immigration (or non-host country of birth) as a likely moderator of the impact of these four resources.
Ethnic identity
According to Erikson (Reference Erikson1968), achieving a stable and well integrated identity is the major psychosocial task of adolescence. Subsequent theory and research has highlighted the multidimensionality of the identity construct, and the importance, especially for members of ethnic minority groups, of achieving a clear and positive sense of their ethnic identity (Phinney & Ong, Reference Phinney and Ong2007; Rivas-Drake et al., Reference Rivas-Drake, Seaton, Markstrom, Quintana, Syed and Lee2014). Phinney and Ong cite Tajfel's (Reference Tajfel1981, p. 255) definition of ethnic identity, namely ‘that part of an individual's self-concept which derives from [his] knowledge of [his] membership of a social group (or groups) together with the value and emotional significance attached to that membership’ (p. 271). Studies have demonstrated that a strong ethnic identity is negatively associated with distress in ethnic minority groups (e.g., Gaylord-Harden, Ragsdale, Mandara, Richards, & Petersen, Reference Gaylord-Harden, Ragsdale, Mandara, Richards and Petersen2007; Rivas-Drake et al., Reference Rivas-Drake, Seaton, Markstrom, Quintana, Syed and Lee2014; Williams, Chapman, Wong, & Turheimer, Reference Williams, Chapman, Wong and Turkheimer2012) and in migrants (Nesdale, Rooney, & Smith, Reference Nesdale, Rooney and Smith1997), an effect that may be due to the role of ethnic identity in bolstering coping resources and reducing adverse effects of discrimination (Williams, Chapman, Wong, & Turkheimer, Reference Williams, Chapman, Wong and Turkheimer2012).
Parental support
Having supportive parents has been shown to be a protective factor in samples drawn from the broad community (Hall-Lande, Eisenberg, Christenson, & Neumark-Sztainer, Reference Hall-Lande, Eisenberg, Christenson and Neumark-Sztainer2007), first-generation migrant adolescents (Harker, Reference Harker2001), and youth from minority ethnic backgrounds (Bekteshi, Xu, & Tran, Reference Bekteshi, Xu and Tran2010; Gaylord-Harden et al., Reference Gaylord-Harden, Ragsdale, Mandara, Richards and Petersen2007).
Peer support
Peer support is positively correlated with numerous mental health indices (Malecki & Demaray, Reference Malecki and Demaray2002) in samples of adolescents in general (Hall-Lande, Eisenberg, Christenson, & Neumark-Sztainer, Reference Hall-Lande, Eisenberg, Christenson and Neumark-Sztainer2007), adolescent migrants (Gagne et al., Reference Gagne, Shapka and Law2014), and adolescent refugees (Correa-Velez et al., Reference Correa-Velez, Gifford and Barnett2010).
School membership
School connectedness, belonging, or membership has been associated with enhanced wellbeing in youth in general (Hall-Lande et al., Reference Hall-Lande, Eisenberg, Christenson and Neumark-Sztainer2007; Juvonen, Reference Juvonen, Alexander and Winne2006) and migrant youth (Chun & Mobley, Reference Chun and Mobley2014; Shoshani et al., Reference Shoshami, Nakash, Zubida and Harper2016). Other research (e.g., Walton & Cohen, Reference Walton and Cohen2011) has shown that a sense of belonging to their school is an important protective factor in the wellbeing of children from minority backgrounds.
The evidence reviewed above makes a strong case for the likely main effects of each of the psychosocial resources on the adjustment of adolescents in general, and migrant adolescents more specifically. In addition, there is evidence (e.g., Gagne et al., Reference Gagne, Shapka and Law2014; Williams et al., Reference Williams, Chapman, Wong and Turkheimer2012) that these resources may be more highly protective of wellbeing among members of ethnic minority groups than among members of the dominant culture. Although limited research has investigated the role of country of birth in moderating these effects, a case can be made for expecting migrant status to accentuate the positive effects of each of these psychosocial resources (c.f. Cristini et al., Reference Cristini, Scacchi, Perkins, Bless and Vieno2015) This case rests upon the likelihood that, relative to their native-born peers, migrant adolescents (a) face greater challenges and threats to their wellbeing, and (b) may have less social and economic capital with which to manage these challenges and threats. In such circumstances, migrant adolescents are likely to rely more heavily upon the resources they do possess, and hence such resources will be disproportionately impactful on their psychological adjustment (Gagne et al., Reference Gagne, Shapka and Law2014). Moreover, to the extent that they face particularly great challenges, this enhanced effect will be stronger in migrants originating from countries where other languages predominate than in those that share a first or official language with the host nation.
Current Study
The aims of the current study were threefold: first, to assess levels of wellbeing and depression in adolescents born in the host country (Australia), other English-speaking countries, and non-English-speaking countries; second, to examine the relationships between these adjustment variables and four psychosocial resource factors; and third, to investigate the moderating effects of country of birth on the relationships between these psychosocial resources and adjustment indices. Three hypotheses were tested:
-
1. (a) Ethnic identity (b) parental support, (c) peer support, and (d) a sense of school membership are positively associated with adolescent wellbeing and negatively associated with adolescent depressive symptoms.
-
2. Psychological adjustment is greater in adolescents born in nations that share the first language of their host country than in adolescents from countries that have a different dominant language.
-
3. The four psychosocial resources are more strongly related to adolescent adjustment (a) in migrant than in native-born adolescents, and (b) in migrants from countries that have a different dominant language than in migrants from countries that share their first language with the host nation.
Method
Participants
Participants were 327 state high school students aged 11 to 17 years (M = 13.70, SD = 1.25). All students attending school on the days of testing whose parents had given (passive) consent were included. They comprised 208 males (63.6%), 118 females (36.2%), and one of unknown gender. There were 64 Grade 7 students, 58 from Grade 8, 92 from Grade 9, and 113 from Grade 10. English was the first language spoken by 74.3% of the students. A total of 150 (45.9%) participants were born in Australia, 105 were born in another English-speaking country (mostly New Zealand, n = 88), and 72 were born in one of 15 Asian, Middle Eastern, African, or South American nations where English is not the main language. Members of the migrant subsample had resided in Australia for between 1 month and 15.5 years (M = 4.73 years, SD = 3.94 years).
The gender composition of the three country of birth groups differed: 69% of the Australian-born and 65% of the other English-speaking nation groups were males, compared to 51% of those born in non-English-speaking countries, χ2(2, N = 327) = 8.03, p = .02, Cramer's V = .16. In addition, the two groups of migrant adolescents differed in the duration of their residence in Australia: those born in English speaking countries (M = 5.42 years, SD = 3.73) versus those born in non-English speaking countries (M = 2.57 years, SD = 2.83), t(159) = 5.21, p < .0005, d = 0.86.
Materials
Our questionnaire contained demographic questions, as well as six multi-item scales, all of which were scored by averaging responses, such that high scores indicated higher levels of the focal characteristic.
The WHO Well-Being Scale-5 (Heun, Burkart, Maier, & Bech, Reference Heun, Burkart, Maier and Bech1999) was used to measure subjective wellbeing. Heun et al. (Reference Heun, Burkart, Maier and Bech1999) reported that this five-item scale (e.g., ‘I have felt cheerful and in good spirits’) has a coefficient alpha of .95.
Depression was measured using the depression subscale of the Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale-21 (Lovibond & Lovibond, Reference Lovibond and Lovibond1995). This subscale includes seven items such as ‘I feel downhearted and blue’. The authors report its coefficient alpha in their normative sample as α = .81.
Ethnic identity was measured by the Multigroup Ethnic Identity Measure — Revised scale (MEIM-R; Phinney & Ong, Reference Phinney and Ong2007). This six-item scale (e.g., ‘I feel a strong attachment towards my own ethnic group’) has an alpha reliability of .87. Although some past research suggests that this scale comprises two dimensions (Phinney & Ong, Reference Phinney and Ong2007; Rivas-Drake et al., Reference Rivas-Drake, Seaton, Markstrom, Quintana, Syed and Lee2014), principal axis factoring, with oblique rotation of the current data revealed a single factor with an initial eigenvalue of 3.65, accounting for 60.9% of the variance. This suggests that a composite measure better captured the participants’ responses than did two specific dimensions.
The 10-item parental support and classmate support subscales of the Child and Adolescent Social Support Scale (CASSS; Malecki & Demaray, Reference Malecki and Demaray2002) were used to measure these variables. Malecki and Demaray reported coefficient alphas of .89 and .94 for the parental support and classmate support scales respectively. Sample items are ‘My parent(s) help me make decisions’ and ‘My classmates treat me with respect’.
School membership was measured by a 12-item short version of the Sense of School Membership Scale — Abridged (Goodenow, Reference Goodenow1993). The original 18-item scale (e.g., ‘People at this school are friendly with me’) has internal consistency values between .78 and .95.
Procedure
After gaining ethics clearance from the school and university, school administrators distributed information to parents regarding the study and invited parents to opt out if desired. Questionnaires were administered online in non-interacting class groups under the supervision of teachers and members of the research team.
Results
Table 1 presents descriptive statistics and correlations. All scales displayed adequate reliability. Correlations between the composite scale variables were small to moderate and statistically significant, except for the relationship between ethnic identity and depressive symptoms. Thus, with this exception, the findings are consistent with the H1 prediction that each of the four psychosocial resources would be positively correlated with wellbeing and negatively correlated with depression.
Table 1 Descriptive Statistics and Correlations

Note: Where applicable, Cronbach alpha reliability coefficients appear on the diagonal.
a Gender: 0 = male, 1 = female. bResidence = Total lifetime (years) residing in Australia. N = 176 only, because this question was not asked of Australian-born participants.
c Main language spoken at home: 0 = English, 1 = another language.
*p < .05. **p < .01. ***p < .001. (two-tailed).
Males reported higher wellbeing than did females. There were no other gender or age differences in wellbeing or depression. Sense of school membership was correlated with age and school year level. Fathers’ and mothers’ levels of educational attainment, a rough proxy for socio-economic status, were not correlated with any of the core variables (all rs < .09, ns).
Main Effects of Country of Birth (COB)
Associations between country of birth (Australia vs. other English-speaking nation vs. non-English-speaking nation) and the study variables were tested by separate one-way analyses of variance (ANOVA). As shown in Table 2, these analyses revealed a significant effect of COB on wellbeing and ethnic identity, but not on the remaining four variables. Post-hoc tests indicated that the students who were born in other English-speaking countries reported higher levels of wellbeing and ethnic identity than did either Australian-born students or students born in non-English speaking countries. The latter two groups did not differ on either wellbeing or ethnic identity.
Table 2 Means (Standard Deviations) of the Study Variables for the Three Country of Birth Groups
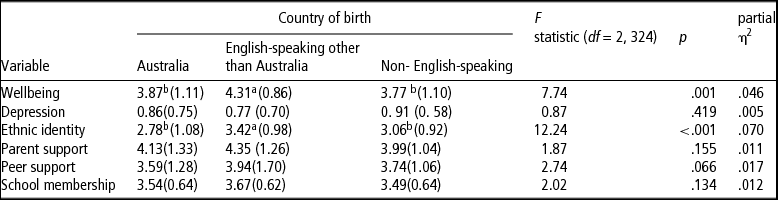
Note: Means within rows that do not share superscripts differ significantly (p < .05, Bonferroni adjusted).
Analyses were repeated comparing scores on all study variables between just the two groups of migrant adolescents, and controlling for duration of residence in Australia. In this case, while the difference in ethnic identity was no longer significant, participants born in English-speaking countries reported greater wellbeing than did those born in non-English speaking countries, F(1, 158) = 11.48, p < .001, partial η2 = .068.
Moderating Effects of Country of Birth
Eight hierarchical multiple regression analyses were conducted to investigate the role of COB in moderating the relationships between the psychosocial resources and the adjustment indices. Two dummy-coded variables were created: COB-English (participants born in an English speaking country other than Australia = 1; all other participants = 0) and COB-NonEnglish (participants born in a non-English speaking country = 1; all other participants = 0). Thus, Australian-born was the baseline group in all analyses. Eight interaction terms were constructed by multiplying each centred psychosocial resource variable with each of the dummy variables. In all regression models, the four psychosocial variables were entered at step 1, the two dummy COB variables were entered at step 2, and two psychosocial resource × dummy variable interaction terms (both involving the same psychosocial resource) were entered at step 3. Major interest lies in step 3, the moderation effects, but results from the first two steps are reported first.
At step 1, 24.3% of the variance in wellbeing, and 14.7% of the variance in depression, was explained by the four psychosocial resource variables (both ps < .0005). At this step, controlling for other psychosocial resources, three of the psychosocial variables predicted wellbeing: parental support (β = .20, p < .0005, sr 2 = .04), peer support (β = .18, p = .003, sr 2 = .03), and school membership (β = .18, p =. 003, sr 2 = .03), while ethnic identity did not (β = .09, p = .09, sr 2 = .01). In predicting depression, school membership (β = -.22, p = .001, sr 2 = .03) and peer support (β = -.20, p = .002, sr 2 = .03) were significant, parental support was not (β = -.07, p = .22, sr 2 = .004), and ethnic identity displayed a significant effect in the direction opposite to its zero-order correlation (β = .15, p = .009, sr 2 = .02).
At step 2, a further 1.9 % of the variance in wellbeing was explained by the two country of birth dummy variables (p = .018), with COB_English significant (β = .12, p = .03, sr 2 = .01), and COB_NonEnglish not so (β = -.04, p = .42, sr 2 = .002). The dummy variables accounted for negligible additional variance in depressive symptoms (ΔR 2 = .003).
Table 3 summarises results from the third step in each of these regression analyses. As shown, the pair of interaction terms entered at step 3 was associated with a significant gain in explained variance in three of the eight regression models. Seven of the 16 specific interaction terms were significant at the p < .05 level. Most (five out of these seven significant interactions) involved wellbeing. Of special note, all four interactions involving school membership were significant.
Table 3 Moderating Effects of Two Country of Birth Dummy Variables on the Relationships Between Each of the Psychosocial Resources and Adjustment Criteria
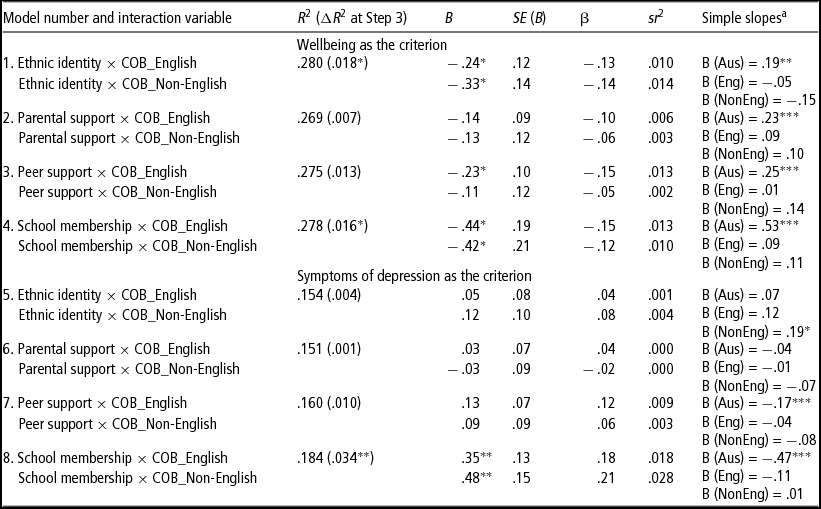
Note: aSimple slopes for participants born in Australia (Aus), in an English-speaking country other than Australia (Eng), and in a Non-English-speaking country (Non).
*p < .05, ** p < .01, **p < .001.
Simple slopes analyses did not support hypothesis 3a. Rather, as shown in the right-hand column of Table 3, the beneficial effects of several of the resources were more pronounced among the Australian-born subsample than among either of the two migrant groups. This was particularly true for school membership. Also of note, contrary to expectations, there was no evidence of a strong protective effect of ethnic identity among the migrant groups.
To test hypothesis 3b, eight additional moderated regression analyses were conducted, as above, except that (a) these analyses included only one dummy COB variable (representing just the two migrant groups, 0 = COB-English, 1 = COB-NonEnglish; n = 178), and (b) duration of residence was entered as a control variable at step 1. In none of these analyses was the country of birth × psychosocial resource interaction term significant (all ps > .20). This shows that the impact of the four psychosocial resources did not vary between migrant adolescents born in English-speaking countries and those born in non-English-speaking countries.
Given the relatively strong protective effects of several of the resources in the adjustment of the Australian-born students, and the generally weak effects associated with ethnic identity, post hoc analyses were conducted using just the Australian-born subsample. These participants were divided into three groups based on their parents’ country of birth: both parents born in Australia (n = 67), one parent born in Australia (n = 39), and neither parent born in Australia (n = 39). (Data on parents’ country of birth were unavailable for five participants.) These ‘second-generation’ analyses revealed significant differences in the means of two of the study variables: ethnic identity (p < .0005) and peer support (p < .01). Post hoc tests showed that Australian-born adolescents who had both parents born overseas (p < .0005), and those with one parent born overseas (p < .05), reported higher ethnic identity than did those with both parents born in Australia. Also, adolescents with either one or two overseas-born parents reported greater peer support than did those with both parents born in Australia (both ps < .05).
Although the small Ns prevented computation of the full regression model in each of these parental-nativity groups, Table 4 presents correlations between each of the resources and the adjustment indices for these groups (with correlations from the whole sample groups included for comparison). Correlations on the left side of this table confirm the generally stronger effects for the Australian-born, than the migrant, adolescents. Comparisons of the correlations on the right side, although not always significant due to lack of power, reveal several interesting results. In particular, ethnic identity had a particularly strong enhancing effect, and school membership had a relatively weak enhancing effect, on the wellbeing of those with both parents born overseas. In addition, parental support was highly protective against symptoms of depression among those with one foreign-born parent, whereas peer support offered little such protection for those with both parents born overseas.
Table 4 Correlations between the Psychosocial Resources and Adjustment Indices for Three Country of Birth Groups, and Three Australian-born Parents’ Country of Birth Groups

Note. For the Australian-born subsamples, correlations within rows that do not share superscripts differ significantly (p < .05).
*p < .05. **p < .01. **p < .001.
Discussion
This study examined wellbeing and depressive symptoms in three groups of adolescents differentiated by their country of birth. Also investigated were the contributions of ethnic identity, parental support, peer support, and sense of school membership in predicting adolescent adjustment, both directly and as moderated by country of birth.
Review of Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1
This stated that the four psychosocial resources are positively correlated with the two adjustment indices. In support, seven of eight correlations were significant in predicted directions, a finding that is broadly consistent with previous studies (e.g., Birman & Chan, Reference Birman and Chan2008; Chao & Otsuki-Clutter, Reference Chao and Otsuki-Clutter2011; Gaylord-Harden et al., Reference Gaylord-Harden, Ragsdale, Mandara, Richards and Petersen2007; Hall-Lande et al., Reference Hall-Lande, Eisenberg, Christenson and Neumark-Sztainer2007; Harker, Reference Harker2001; Wolfradt, Hemple, & Miles, Reference Wolfradt, Hemple and Miles2003; Nesdale, Rooney, & Smith, Reference Nesdale, Rooney and Smith1997). The single non-significant effect, that of ethnic identity on depression, while unexpected, is not entirely at odds with past research showing that ethnic identity is more strongly related to positive wellbeing than to compromised wellbeing (Smith & Silva, Reference Smith and Silva2011).
Hypothesis 2
Little consensus exists in the past research as to the psychological adjustment of migrant adolescents relative to their native-born counterparts, a state of affairs that may reflect the varying realities in different communities around the world, as well as differences in the samples, methods, and measures used in past research. On balance, we expected adolescents migrating from English-speaking countries to report better adjustment than those born in countries in which a different language predominates. In contrast to this second hypothesis, we observed no differences in symptoms of depression between adolescents born in Australia, those born in other English-speaking countries, and those born in non-English-speaking countries, a finding consistent with some past studies (e.g., Derluyn et al., Reference Derluyn, Broekaert and Schuyten2008). However, we found that adolescents born in an English-speaking country other than Australia reported the greatest wellbeing, while there was no difference in the wellbeing of adolescents born in Australia and those born in non-English-speaking countries.
The superior wellbeing of adolescents from other English-speaking countries may be partly explained by the size and mix of adolescents comprising this subgroup. As previously reported, 88 of these 105 students were New Zealand-born. Not only was their reported wellbeing higher than that of other groups, so too was their ethnic identity. It seems that the numeric size of this minority group, buoyed by shared connections to their ethnic background, served to bolster members’ sense of wellbeing. The finding may thus be understood not so much as an ethnicity effect, but as an ethnicity within context (Bellmore et al., Reference Bellmore, Witkow, Graham and Juvonen2004), or ethnic congruence (Demanet, Van Praag, & Van Houtte, Reference Demanet, Van Praag and Van Houtte2016) effect. That is, in school contexts such as this, membership of a minority, but nonetheless quite large and cohesive subgroup, may confer an adjustment advantage over members of both the majority group and other, more fractured minority groups.
While this could be viewed as an isolated case, there exist many school and other social contexts that are inhabited by large numbers of one or more minority ethnic groups. Such ‘majority minority’ contexts may be conducive to healthy migrant effects, or at least to the avoidance of migrant morbidity effects. For example, Motti-Stafanidi et al. (Reference Motti-Stafandi, Pavlopoulos, Obradovic, Dalla, Takis, Papathanassiou and Masten2008) found evidence of a migrant morbidity effect on adolescent grades and popularity in a Greek school where migrant students were heavily outnumbered, but no such effect in a nearby school in which the migrant group was present in larger numbers.
Hypothesis 3
This hypothesis stated that relationships between psychosocial resources and adjustment are moderated by country of birth, with these resources providing greater benefits to migrant adolescents (especially those born in non-English-speaking countries) than to their native-born peers. The hypothesis was not supported. For wellbeing, the effects of three of the four resources showed some level of moderation by adolescents’ country of birth, while for depressive symptoms, the effects of just school membership were moderated by country of birth. In all seven cases in which the interaction was significant, the psychosocial resource had a stronger protective effect among the Australian-born than among the migrant subsamples. Moreover, contrary to the hypothesis, the strength of these moderated effects did not differ between the two subsamples of migrant adolescents.
This clear trend for psychosocial resources to be more closely related to adjustment in Australian-born than in migrant adolescents raises questions regarding sources of support that might particularly advantage foreign-born adolescents. Resources not investigated in the present study but possibly contributing disproportionately to the adjustment of migrant adolescents include provision of teacher support (Demanet, Van Praag, & Van Houtte, Reference Demanet, Van Praag and Van Houtte2016), close extended family ties, integration into ethnic community life, and high levels of religiosity (Dimitrova & Aydinli-Karakulak, Reference Dimitrova and Aydinli-Karakulak2016; Harker, Reference Harker2001). Consistent with the first of these suggestions, Kabir and Rickards (Reference Kabir and Rickards2006) found that, compared to other at-risk groups, students from refugee backgrounds were more likely to identify as sources of support people outside their immediate family, including their English teacher, pastoral care teacher, and school principal.
Given the unexpected current results, the subsample of Australian-born adolescents was further split into groups based on their parents’ nativity. Group sizes were small, and findings require replication. Nonetheless, these analyses are instructive. For example, although the sample of 150 Australian-born adolescents, as a whole, reported relatively low levels of ethnic identity, that subset of Australian-born adolescents (n = 39) who had two foreign-born parents showed the strongest positive effect of ethnic identity upon wellbeing of any group in the study. This makes sense in that this second-generation group, more than others, may be torn between different cultural and ethnic allegiances (Kao, Reference Kao and Hernandez1999). Similarly, the strongest of all effects of parental support was among Australian-born adolescents who have one foreign-born parent. Again, possibly in hindsight, there is sense in the notion that these adolescents especially benefit from parental support. Thus, while past research (Chun & Mobley, Reference Chun and Mobley2014; Harris, Reference Harris and Hernandez1999; Kao, Reference Kao and Hernandez1999) has highlighted the elevated risk and morbidity levels of second-generation migrants, the current study adds to knowledge of factors that possibly protect against these risks. More intriguingly, current findings suggest that adolescents whose parents were born in different countries may benefit from different psychosocial resources (e.g., ethnic identity vs. parental support). Such a proposition is consistent with the notion of person-environment fit, or immigration stage-environment fit (Eccles, Reference Eccles, Lerner and Steinberg2004; Gagne et al., Reference Gagne, Shapka and Law2014), in that students benefit most from resources that match their particular psychosocial and acculturative needs.
Limitations and Future Research
The results should be interpreted in light of several limitations. First, the study used a cross-sectional design and thus could not establish the presence or direction of causal effects. Multi-wave longitudinal studies would assist in identifying temporal (if not causal) relations, while studies involving a larger sample of participants drawn from a wider range of schools would provide a clearer picture as to the psychological adjustment of migrant adolescents.
Second, we did not distinguish between types of immigration such as refugee, skilled, and family immigration. While the term ‘migrant’ refers to anyone who has left their home country, past researchers (Stevens & Vollebergh, Reference Stevens and Vollebergh2008) have found differences between the mental health of those who were forced to migrate (as refugees) and those who chose to migrate, a finding typically attributed to the greater likelihood of preimmigration traumatic experiences in the refugee group. Larger samples that permit finer differentiation between different types, causes, and sources of immigration are recommended in future studies.
Third, we computed a composite ethnic identity score for each participant, rather than separate exploration and commitment scores as suggested by Phinney and Ong (Reference Phinney and Ong2007) and past research (Rivas-Drake et al., Reference Rivas-Drake, Seaton, Markstrom, Quintana, Syed and Lee2014). Use of a single ethnic identity dimension was supported by factor analysis of our data set. It is possible, however, that responses to the MEIM-R scale were influenced by a ‘satisficing’, or heuristic-based, bias (Krosnick, Reference Krosnick1999), in which participants drew on global attitudes to their ethnic group (e.g., attitudes of positive or negative regard) to respond to all items in a like manner without discriminating sufficiently between them. If true, the operation of this bias helps to explain the evident unidimensionality of the scale as currently used, and the unexpected nature of some of the results pertaining to ethnic identity. Future research may involve controlling this source of bias while assessing the moderated effects of more specific ethnic identity dimensions.
Like much research, the current study sheds light on some questions, but poses others. For example, while the study shows that a healthy migrant effect may exist in one, but not in other, migrant subgroups of a larger sample, it leaves unanswered the question of whether the obtained healthy migrant effect was due more to cultural and linguistic similarity to the host nation, or to subgroup size and cohesion. To answer this question, future research requires samples large enough to split migrants from English-speaking nations into two groups: those from nations that are more, versus less, numerically strong within the particular school context. Similarly, the study showed that while native and migrant adolescents report similar levels of school belonging, this resource seems to confer a greater adjustment advantage on native rather than foreign-born students. Research is needed not only to test the robustness of this effect, but also to identify reasons for its existence: Which aspects of school culture or identity benefit students born in the host country more so than other students? Do migrant students have available an especially rich or wide array of community and family resources, and are thus less reliant on school-based support?
Implications
The findings have implications for developing strategies to promote adolescents’ psychological adjustment. All four psychosocial resources were positively associated with wellbeing, and all but ethnic identity were negatively associated with depression. Regression analyses demonstrated that most of these effects were unique (additive), rather than duplicative. This suggests that interventions aimed at promoting ethnic, parent, peer, and school resources might enhance psychological adjustment, with a multipronged program likely to be more efficacious than one that seeks to bolster just one of the resources (Greenberg et al., Reference Greenberg, Weissberg, O'Brien, Zins, Fredericks, Resnik and Elias2003).
The overriding message from the present study relates to the importance of building sources of social/relational support. Interventions can be implemented in a range of settings (home, school, community) using multiple approaches (agents, media, formats). Outdoor adventure camps, for example, have been shown to have lasting benefits for participant acceptance, trust, and communication skills (Hattie, Marsh, Neill, & Richards, Reference Hattie, Marsh, Neill and Richards1997). A sense of connectedness to school and family can be enhanced through mentoring interventions (Karcher, Reference Karcher2005). More generally, a small school size, an inclusive school climate, use of cooperative learning methods, and student participation in extracurricular activities have each been shown to increase adolescents’ sense of belonging and engagement (Eccles, Reference Eccles, Lerner and Steinberg2004; Steinberg, Reference Steinberg2017). Policies and practices that build safe communities and schools (e.g., anti-bullying, and anti-discrimination programs) can also contribute.
Conclusion
Set in a mixed ethnicity Australian secondary school, this study provided evidence of the immigrant paradox phenomenon in that children born in English-speaking countries had higher levels of wellbeing than did native-born (and other migrant) youth. The study also identified quite robust relationships between four psychosocial resource variables and two psychological adjustment indices. As such, the findings suggest that the adjustment of adolescents can be enhanced through interventions designed to bolster these resources. Importantly, several of the resources-adjustment relationships were moderated by adolescent country of birth, with a sense of school membership, in particular, having disproportionately favourable effects for Australian-born adolescents. The study thus highlights the ongoing need to identify sources of support that especially benefit adolescents from non-English-speaking backgrounds.






