Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 March 2022
A local positional system (LPS) is proposed, in which particles are launched at given velocities, and a sensor system measures the trajectory of the particles in the platform frame. These measurements allow us to restore the position and orientation of the platform in the frame of the rotating Earth, without solving navigation equations. When the platform velocity is known and if the platform orientation stays the same, the LPS technique allows a navigational accuracy of 100 $\mu$ m per one hour to be achieved. In this case, the LPS technique is insensitive to the type of platform trajectory. If there are also velocimeters installed on the platform, then one can restore the platform velocity and angular rate of the platform rotation with respect to the Earth. Instead of navigational equations, it is necessary to obtain the classical trajectory of a particle in the field of a rotating gravity source. Taking into account the gravity-gradient, Coriolis, and centrifugal forces, the exact expression for this trajectory is derived, which can be widely used in atomic interferometry. A new iterative method for restoring the orientation of the platform without using gyroscopes is developed. The simulation allows us to determine the conditions under which the LPS navigation error per hour is approximately $10$
m per one hour to be achieved. In this case, the LPS technique is insensitive to the type of platform trajectory. If there are also velocimeters installed on the platform, then one can restore the platform velocity and angular rate of the platform rotation with respect to the Earth. Instead of navigational equations, it is necessary to obtain the classical trajectory of a particle in the field of a rotating gravity source. Taking into account the gravity-gradient, Coriolis, and centrifugal forces, the exact expression for this trajectory is derived, which can be widely used in atomic interferometry. A new iterative method for restoring the orientation of the platform without using gyroscopes is developed. The simulation allows us to determine the conditions under which the LPS navigation error per hour is approximately $10$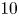 m.
m.