Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 January 2020
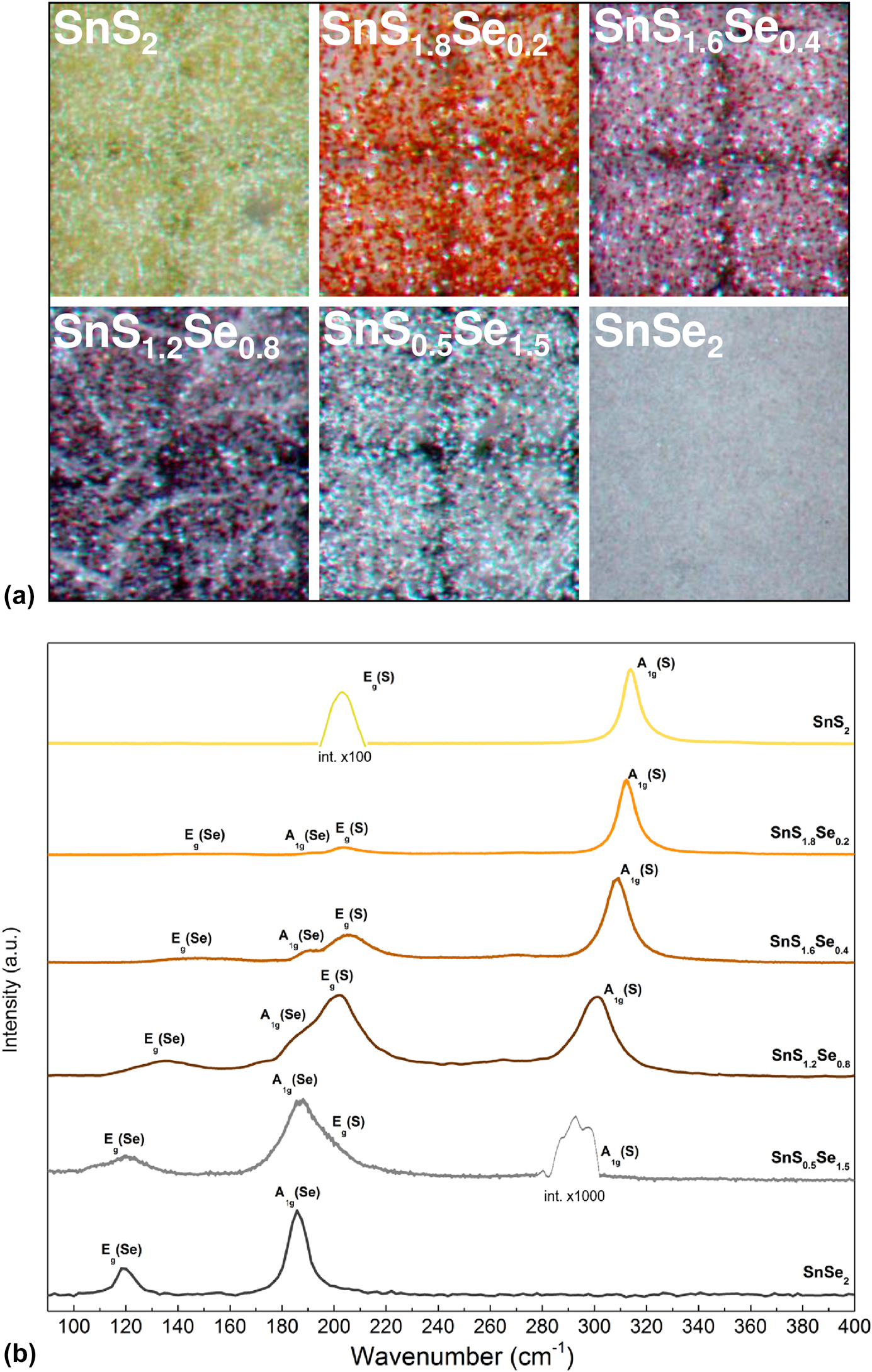
Epitaxial SnSxSe2−x films with tunable band gap energies (1.0–2.2 eV) are of growing interest for photodetectors and 2D heterostructures for nanoscale electronics. In this study, powder vapor transport growth of SnSxSe2−x was investigated on c-plane sapphire and epitaxial graphene (EG)/6H–SiC substrates using tin, sulfur, and selenium powder sources in a heated tube furnace. The SnSxSe2−x composition was controlled by varying the sulfur and selenium source temperatures and the corresponding chalcogen vapor pressure ratio. Raman spectroscopy was used to determine the alloy composition of the films, and the optical properties were characterized using UV-Vis-NIR spectroscopy. SnSxSe2−x grown on sapphire consisted of vertically oriented platelets. By contrast, large-area, planar coalesced SnSxSe2−x films grew on EG with low surface roughness indicative of a van der Waals growth mode. High-resolution X-ray diffraction θ–2θ scans and pole figure analysis confirm that the SnSxSe2−x films are c-axis oriented with epitaxial relation being  $\left[ {11\bar{2}0} \right]$ SnSxSe2−x‖
$\left[ {11\bar{2}0} \right]$ SnSxSe2−x‖ $\left[ {10\bar{1}0} \right]$ 6H–SiC.
$\left[ {10\bar{1}0} \right]$ 6H–SiC.
This author was an editor of this journal during the review and decision stage. For the JMR policy on review and publication of manuscripts authored by editors, please refer to http://www.mrs.org/editor-manuscripts/.