Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 March 2011
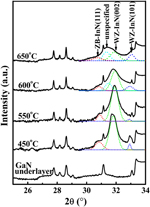
InN thin films were grown on GaN underlayer with sapphire substrate by metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy under different growth conditions, including growth temperature, reactor pressure, and V/III ratio. X-ray diffraction and Raman scattering measurements reveal that the samples grown at different temperatures are mixed with different phases, especially at higher temperature. The calculated phonon dispersion curves of wurtzite, zinc-blende, and rocksalt structures show that the samples mainly contain wurtzite structure and small amount of zinc-blende phase, while the samples grown at 600 °C and 650 °C include a new structural phase other than the three well-known ones. This analysis demonstrates that the InN epilayer grown at 550 °C has the highest phase purity and better crystalline quality. Besides the key role of growth temperature, a relatively higher reactor pressure and lower V/III ratio are found to be more conducive to the improvement of crystalline quality, though they have a modest effect on the InN microstructure.