Article contents
Strain induced hardening and softening behaviors of deformed Cu and Cu–Ge alloys
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 February 2016
Abstract
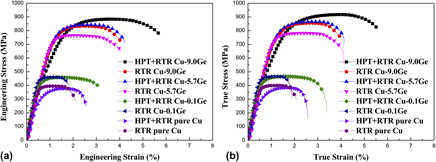
Herein, Cu and Cu–Ge alloys with different stacking fault energies (SFEs) are prepared via rolling at room temperature (RTR) and via a combination of high-pressure torsion (HPT) and RTR (HPT + RTR). The x-ray diffraction measurements reveal that the grain size, dislocation density, and twin density vary with the strain and SFEs. The tensile tests indicate that the strength of materials with medium SFEs increases initially and then slightly declines, while the ductility is enhanced by increasing the strain via HPT. In contrast, for low-SFE materials, enhanced strength and improved ductility may be achieved simultaneously through increasing the strain to a high level. The variation of strength with respect to strain is primarily dependent on the solute concentration and SFE. The underlying mechanisms governing the effect of strain and SFE on the microstructures and mechanical properties of the metals are also discussed.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by


