Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 January 2014
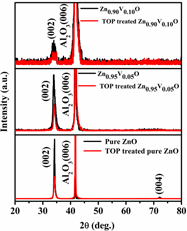
In the present study, we report an activation and enhancement of room temperature ferromagnetism in pure ZnO and V-doped ZnO (Zn0.95V0.05O and Zn0.90V0.10O) thin films by trioctylphosphine (TOP) functionalization. X-ray diffraction patterns show a slight decrease in the intensity of the diffraction peak on TOP functionalization. Atomic force micrographs of pure and V-doped ZnO films reveal no disorder in the film surface on TOP functionalization. The chemical bond formation of TOP on ZnO film surface was examined by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy measurements. Photoluminescence measurements of TOP-functionalized ZnO films show enhancements of UV emission and quenching of visible emission. TOP-functionalized ZnO films reveal enhanced ferromagnetic behavior as evidenced from vibrating sample magnetometer measurements.