Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 August 2015
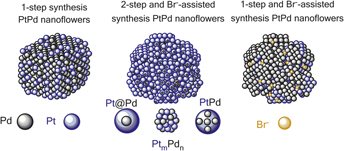
This work aims to synthesize PtPd catalytic clusters and to study the effect of the particle size, the curvature and possible alloying on the catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction, electrochemical stability, the mass-transfer of redox active species toward catalytic sites and the electro-kinetic of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) process. The curvature and the chemical composition of the catalyst surface significantly influence the electrochemically active surface area and catalytic activity toward oxygen reduction, regardless the particle size. The best catalytic activity was accomplished for 45 nm clusters due to possible alloying that enhance the O2 adsorption and dissociation. The complementary impedance studies demonstrated that 45 nm cluster has also the shortest effective diffusion length and the highest reaction rate constant among all morphologies, indicating on superior reactant transport to the catalytic sites. In addition, the 45 nm clusters showed improved electrochemical stability that is believed to be the combined effect of alloying and the compactness of the structure.