Article contents
On the determination of hardness and elastic modulus in BaFe2As2 lamellar-like material
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 May 2016
Abstract
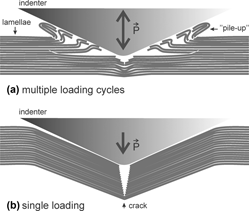
The mechanical behavior of superconductor lamellar-like BaFe2As2 single crystals was investigated at nanoscale by instrumented indentation. The unique responses of the ab- and a(b)c-crystallographic planes were discussed based on their influence in hardness (H) and elastic modulus (E). The results allowed two main conclusions. (i) The choice of testing parameters strongly affected the scaling of mechanical properties on the lamellar surfaces. Lamellar cracking was the leading mechanism of deformation, featuring a brittle-like behavior and affecting considerably H and E. However, the plastic deformation history allowed different elastic–plastic responses on the ab-plane owing to the compaction of the material. Threshold loads for cracking depended on both loading rate and penetration velocity, pointing out to time-dependent plastic deformation mechanisms. (ii) Proper estimates were achieved for H in multiple loading tests [3.4 GPa for ab- and ∼1 GPa for a(b)c-planes], and for E under loads less than 3 mN (∼55 GPa for both planes).
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by



