Article contents
Observation of compound semiconductors and heterovalent interfaces using aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 August 2016
Abstract
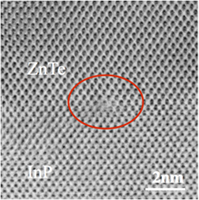
This paper reviews our recent investigations of compound semiconductors and heterovalent interfaces using the technique of aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy. Bright-field imaging of compound semiconductors with a collection angle that is comparable in size to the incident-beam convergence angle is demonstrated to provide better atomic-column visibility for lighter elements in comparison with the more traditional high-angle annular-dark-field approach. Several pairs of Group II–VI/Group III–V compound semiconductors with zincblende structure have been studied in detail. These combinations are all valence-mismatched (i.e., heterovalent), and include CdTe/InSb (Δa/a ≤ 0.05%), ZnTe/InP (Δa/a = 3.8%), and ZnTe/GaAs (Δa/a = 7.4%). CdTe/InSb (001) interfaces are observed to be defect-free with a slight lattice contraction at the interface plane. For interfaces with larger lattice-parameter mismatch, the primary interfacial defects are identified as Lomer edge dislocations and perfect 60° dislocations. However, the atomic structure of the dislocation cores has not yet been unambiguously determined.
- Type
- Invited Feature Paper
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 32 , Issue 5: Focus Issue: Aberration Corrected Transmission Electron Microscopy , 14 March 2017 , pp. 921 - 927
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Eric Stach
This paper has been selected as an Invited Feature Paper.
References
REFERENCES
- 7
- Cited by



