Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 June 2019
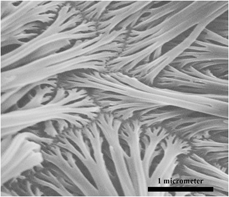
Nowadays, hierarchical materials have received tremendous interests because of their unique physical and chemical properties. In this article, a novel and facile particle aggregation method was used to fabricate vertically aligned diamondoid nanowires and hierarchical branched nanowire cluster array by using an electrophoresis template method. Triamantane, a three-cage diamondoid, was applied as raw material in current research. Diamondoids are nanometer-sized, hydrogen-terminated diamond-like, saturated hydrocarbons, which process great potential in nanotechnology due to biocompatibility and ultrahard nature. By electrophoresis template method, triamantane molecules dissolved in toluene were transferred into a porous alumina template by electric field and form the one-dimensional (1D) nanostructure with high aspect ratio. After that, a two-step thermal treatment was applied to the nanowires to achieve hierarchical branched nanowires. The surface morphologies of triamantane nanowire array with different treatments were characterized by scanning electron microscopy. This approach opens a new avenue for mass production of the vertically aligned diamondoid nanowires and hierarchical branched nanowire cluster arrays.