Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 February 2019
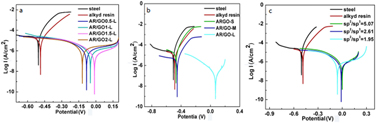
Graphene oxide (GO) is a promising material in improving the corrosion resistance properties of metals. This improvement significantly relies on the microstructure and electrical properties of GO, which nevertheless is rarely studied. Here, multiscale GOs with different flake sizes and oxidation degrees were fabricated and incorporated into waterborne alkyd resin (AR). The physical and chemical structures of GO and AR/GO composites were characterized in detail. Multiscale GOs are successfully prepared, and the corrosion resistance of AR/GO coatings is measured by electrochemical workstation. Electrochemical experiments indicate that GOs with larger flake sizes have excellent barrier properties due to the shielding effect; GOs with appropriate oxidation degrees could effectively improve the dispersion of GO and avoid the conductive path of GO in the matrix, because oxidation degree of GO could influence the dispersion and electrical properties. The corrosion protection efficiency of AR/GO(GO: 120 μm, 1.5 wt%, sp2/sp3 = 2.61) is 98.14%, which is 2.26 times higher than AR. The multiscale effects of GO on the corrosion resistance property of AR coatings are quite general, thus providing guidelines for developing highly efficient corrosion resistant coatings for practical usage.