Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 November 2020
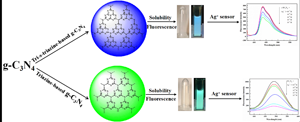
A triazine-based graphite carbon nitride (tri-C3N4) was successfully prepared using a solid and mild method, and modified through concentrated acid and the hydrothermal method. Interestingly, the modified tri-C3N4 (tri-HC3N4) showed good water stability and excellent fluorescence property. Meanwhile, tri-HC3N4 was successfully used to construct a high-sensitive and selective fluorescence sensor to Ag+. The as-prepared fluorescence sensor showed a fast response and a low detection limit as 0.4046 μM. Moreover, the possible quenching mechanisms were discussed based on the photoinduced electron transfer and the formation of new complex between tri-HC3N4 and Ag+ with the help of the related characterizations. This study does not only provide a new tri-HC3N4 for a high efficiency fluorescence sensor, but also show the potential application in biological sciences.