Article contents
Microwave dielectric properties of low loss and highly tunable Ba0.5Sr0.5Ti1−3y/2WyO3 ceramics
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 January 2012
Abstract
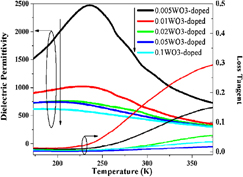
This article reports on microstructure and dielectric properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5Ti1−3y/2WyO3 ceramics. Dielectric peaks of the Ba0.5Sr0.5Ti1−3y/2WyO3 ceramics were markedly suppressed, broadened, and shifted to low temperature with increasing content of W. The limit of W incorporating into the barium strontium titanate (BST) lattice was y = 0.02. Two second phases (BaWO4 and Ba2Ti5O12) were formed above the solid solution limit of W in BST. The doping mechanism represents a new approach to develop microwave tunable materials. Dielectric properties of the Ba0.5Sr0.5Ti1−3y/2WyO3 ceramics could be optimized by the content of W. The sample with y = 0.05 had ε′ of 431, quality factor of 365 (at 2.111 GHz), and tunability of 11.5%, which makes a potential candidate for tunable microwave device applications in the wireless communication.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


