Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 January 2017
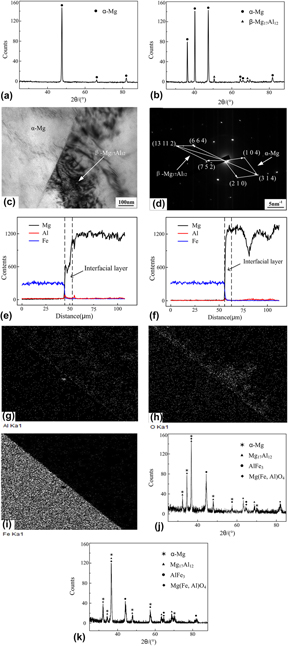
The dissimilar MIG welding of Mg alloy and ultra-high strength steel was investigated. The results indicated that the Mg-steel joints had characteristics of welding-brazing and included weld zone, bond zone, and interface zone. The weld zone with an equiaxed grain structure mainly consisted of α-Mg and α-Mg + β-Mg17Al12 phases when AZ31 and AZ61 filler metals were used respectively. The interface zone presents a double-layer structures: the AlFe3 layer at steel side and the Mg(Fe, Al)O4 + Mg3.1Al0.9 layer at Mg side, and their evolution process has been summarized. The joint strength was improved obviously at the heat input of 1987–2100 J/cm due to eliminating incomplete joining defects and cracks in the interface zone. With AZ61 filler metal, the weld Al content was 6.24%, the joint strength was elevated from 174 MPa for AZ31 filler metal to 201 MPa (83.8% of Mg alloy base metal), which is related to the increased Al promoting the interface reaction.