Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 September 2019
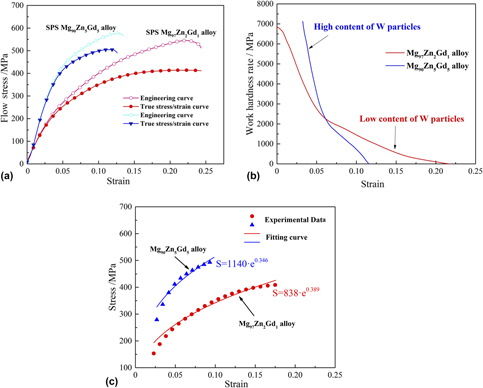
Two rapidly solidified (RS) Mg ribbons with the compositions of Mg97Zn2Gd1 and Mg90Zn5Gd5 (at.%) were first prepared by the planar flow casting method. These RS ribbons were subsequently consolidated by spark plasma sintering (SPS). The use of SPS on the RS ribbons was demonstrated to be an effective processing route to control W-phase precipitation process while keeping fine grains. The size of W-phase particles was less than 200 nm in Mg97Zn2Gd1 alloy and smaller than 500 nm in Mg90Zn5Gd5 alloy. The content of W phase was approximately 34 vol% and 41 vol% in the two SPS bulks, respectively. The compressive properties showed that the yield compressive stress (YCS) and ultimate compressive stress of the Mg97Zn2Gd1 alloy reached 200 MPa and 390 MPa, respectively, and an elongation of 0.24. The corresponding values for the Mg90Zn5Gd5 alloy were 313 MPa, 504 MPa, and 0.14, respectively. Based on the results of the quantitative analysis, W-phase nanoparticles with size less than 100 nm exhibited obviously strengthening effect in the Mg alloys. It highlighted that the W-phase nanoparticles contributed a large proportion of the YCS in the Mg97Zn2Gd1 alloy and a relatively small proportion for that of the Mg90Zn5Gd5 alloy.