Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 April 2012
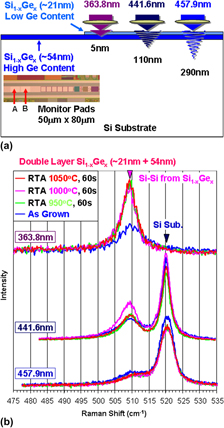
Boron-doped, single (∼54 nm) or double (∼21 + 54 nm) Si1−xGex layers were epitaxially grown on 300-mm-diameter p−-Si(100) device wafers with 20 nm technology node design features, by ultrahigh vacuum chemical vapor deposition. The Si1−xGex/Si wafers were annealed in the temperature range of 950–1050 °C for 60 s to investigate the effect of annealing on possible changes of Ge content and Si stress near the Si1−xGex/Si interface. High spectral resolution, micro-Raman spectroscopy was used as a nondestructive characterization technique with five excitation wavelengths of 363.8, 441.6, 457.9, 488.0, and 514.5 nm. Ge diffusion and generation of compressive stress at the Si1−xGex/Si interface were measured on all annealed wafers. Ge diffusion and the accumulation of compressive Si stress after annealing showed significantly different behaviors between single- and double-layer Si1−xGex/Si wafers. Raman characterization results were compared with secondary ion mass spectroscopy and high-resolution x-ray diffraction results.