Article contents
Low-temperature synthesis and characterization of PVP-capped FeAu nanoparticles
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 June 2011
Abstract
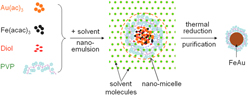
We report the low-temperature synthesis and characterization of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)-capped FeAu magneto-plasmonic multifunctional nanoparticles by a one-step nanoemulsion process. The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy study proves the PVP coating on the surface of the resultant FeAu nanoparticles, whereas the structural, magnetic, and optical analysis illustrates the fusion of iron and gold into one single nanostructure showing the nanoparticle shape and a tight size distribution with an average size of 11.3 nm, followed by the growth habit compared to other relevant nanoparticles. Moreover, the PVP-capped FeAu nanoparticles manifest soft ferromagnetic behavior with a small coercivity of ∼40 Oe at room temperature. The corresponding magnetic hysteresis curves were elucidated by modified bi-phase Langevin equations, which were reasonably interpreted with the binary particle size distribution. The nanoparticles reveal a well-defined surface plasmon resonance band at ∼546 nm and a visual demonstration shows the magnetic separability of all nanoparticles for potential magnetic and/or optical manipulation.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 5
- Cited by


