Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 February 2016
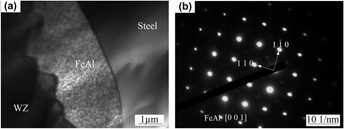
Dissimilar materials of S235JR steel and AZ31B Mg alloy were welded by metal inert-gas arc welding. Interface characteristics and mechanical behavior of intermetallic compound layer at the Mg/steel interface in the welded joint were investigated. The intermetallic compound layer was mainly made up of FeAl phase, which exhibited unequal thickness at different positions in the interface. The growth coefficient of FeAl intermetallic compound layer could be expressed as K = K0 exp(−Q/RT) with Q of 195 kJ/mol. The kinetics of growth of the intermetallic compound layer indicated that its formation and growth were mainly driven by elements diffusion, and hence the thickness of the layer was dependent on peak temperature and reaction time which were determined by welding parameters. The FeAl intermetallic compound layer with high hardness was the weak zone where cracks inclined to derive and propagate during tensile testing. The fracture surfaces displayed both brittle and ductile features.