Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 July 2020
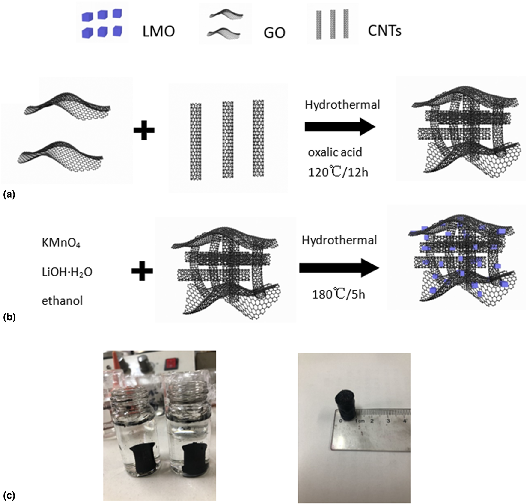
Integrating LiMn2O4(LMO) and different carbon materials to build a mixed cathode system can provide fast transport channels to improve the conduction of both electrons and ions. In this paper, our work studied in situ low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis of LMO nanocomposites based on graphene oxide (GO)/carbon nanotubes (CNTs) hydrogel. Compared with the pure LMO nanoparticles, GO/CNTs/LMO (GCLMO) composites greatly improved electrochemical performance in specific capacity, cycle performance and rate ability. The electrochemical test results showed that the specific capacitance of GCLMO nanocomposites reached 396 F/g at the current density of 0.5 A/g, which was much higher than 221 F/g of pure LMO. Even at the current density of 10 A/g, the specific capacitance was still as high as 309 F/g. Besides, after 2000 cycles, the specific capacitance retention of the composite was 93%. Electrochemical data showed that GCLMO composite is an ideal cathode material for supercapacitors.
Please note a has been issued for this article.