Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 April 2016
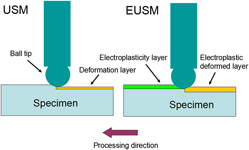
The effect of electropulsing assisted ultrasonic surface modification (EUSM) on microstructure and surface properties of S50C steel welded components is investigated. Compared with conventional ultrasonic surface modification (USM) process, EUSM process achieves significant improvements in microstructure, including deeper strengthened layers and gradient microstructure on the surface. The EUSM-induced microstructure results in higher levels of surface compressive residual stress and greater surface microhardness and its effective depth. Conventional USM process is inevitably accompanied by some plastic damages, such as pit and crack defects. The damages, however, can be eliminated to some extent during the EUSM process. These enhancements may be attributed to the thermal and athermal effects caused by electropulsing treatment, which accelerates the mobility of dislocations in the dynamic recrystallization process.
Contributing Editor: Jürgen Eckert