Article contents
Improved photocatalytic reactivity of ZnO photocatalysts decorated with Ni and their magnetic recoverability
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 May 2015
Abstract
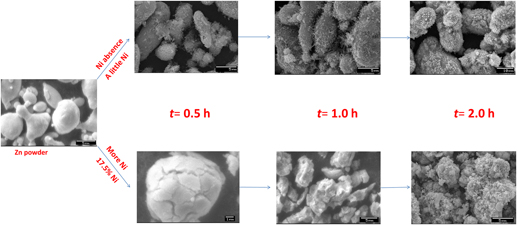
In this paper, the Ni-decorated ZnO photocatalysts with magnetic separable characteristics were prepared by a simple replacing-hydrothermal process for the first time. The as-synthesized composites were characterized by powder x-ray diffraction, UV–visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscopy, and so on. It is found that the introduction of Ni (as Ni0 and Ni2+ forms) turned the morphologies of ZnO photocatalysts, enhanced photoabsorption in a visible light region, and increased amount of surface adsorbed oxygen. The photodegradation test of anthraquinone dye (reactive brilliant blue KN-R) indicated that the Ni-decorated ZnO photocatalysts have better activities as compared to the ZnO reference. The enhancement of photocatalytic activity of Ni-decorated ZnO photocatalysts can be attributed to the existence of Ni2+ doping, Ni0/ZnO heterostructure, and abundant-adsorbed oxygen (as the electronic scavenges), which caused efficient separation of electron–hole pairs in Ni-decorated ZnO photocatalysts. Furthermore, the introduction of metallic Ni also endued ZnO with good magnetic recoverability. The re-collected experiments by external magnetic field indicated that Ni-decorated ZnO as a magnetically recoverable photocatalyst is acceptable.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
REFERENCES
- 5
- Cited by


