Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 October 2018
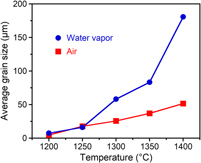
Pressureless sintering is a simple and traditional processing method for producing dense ceramics by heating at a high temperature. The introduction of water vapor into this atmosphere can decrease the sintering temperature and accelerate grain growth. In this work, we report water vapor-assisted sintering of submicrometer titania (TiO2) powder. Dense TiO2 pellets with a relative density over 99% were obtained in 0.1 MPa of water vapor at a lower temperature than in air. The submicrometer particles (∼0.5 µm) grew to an average size of 181 µm after sintering at 1400 °C in water vapor, whereas the particle size obtained by sintering in air was 51 µm. Furthermore, we verified the incorporation of oxygen from water vapor into TiO2 by using isotopically labeled water (H218O). Water vapor-assisted sintering can potentially lead to the production of single crystal-like ceramics by a pressureless route and without any additives.