Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 January 2013
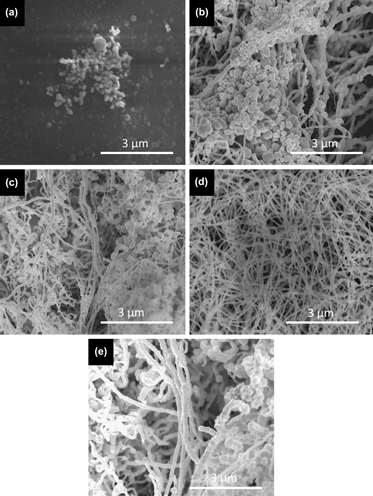
In this study, gold (Au) nanowires were synthesized with a modified hydrothermal process, and high structural purity and control over Au nanowire diameter were achieved. Parametric study was performed to examine the effect of surfactant concentration, reaction time, and temperature on the quality of the synthesized products. The optimum conditions were determined for the synthesis with two different surfactant molecules, namely hexamethylenetetramine and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Au nanowires synthesized under optimum conditions have high aspect ratio (diameters in the range of 50–110 nm and lengths in micrometers) with high structural purity and are potentially useful for applications such as surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy and transparent conducting electrodes for optoelectronic devices.