Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 January 2011
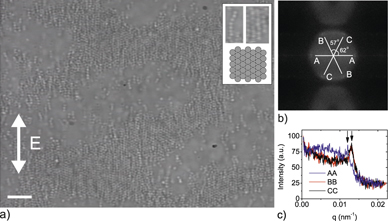
Alternating current (AC) electric fields generated by coplanar electrodes are used to externally direct the assembly of submicrometer sized disk-shaped zeolite particles. At the edge of the electrode, zeolite particles assemble in a brushlike structure that forms because of an interplay between an induced dipolar interaction and the drag force due to AC electroosmotic flow. Far from the electrode edge, where the fluid is quiescent, the disk-shaped particles form a nearly hexagonally close-packed structure, similar to suspensions of spherical particles. These results demonstrate a surprising generality of field-directed structures and offer promise for a hierarchical fabrication of nanostructures from zeolites.