Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 January 2017
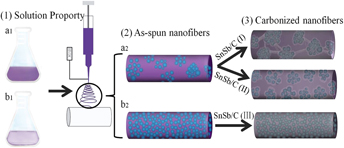
SnSb nanoparticles are dispersed in carbon nanofibers by electrospinning technology and different SnSb precursors, including Sn0.92Sb0.08O2.04 nanoparticles, Sn(CH3COO)2/Sb(CH3COO)3, and SnCl4·5H2O/SbCl3, are used to tune the morphology of the resultant SnSb/C nanofibers. Porous SnSb/C nanofibers are formed during carbonization Sn0.92Sb0.08O2.04 nanoparticles and Sn(CH3COO)2/Sb(CH3COO)3 are used as precursors of SnSb, while solid nanofibers are observed with SnCl4·5H2O/SbCl3 as the precursor indicating the formation mechanism is closely related to the properties of SnSb precursors. Excellent cycling preference (99% capacity retention after 200 cycles) and high coulombic efficiency (above 99% after 10 cycles) are obtained for the SnSb/C nanofibers using Sn0.92Sb0.08O2.04 as precursor, due to its high surface area and stable SnSb/C structure. It is demonstrated that the uniquely designed composite nanofiber structure with excellent lithium storage performance can be realized simply by selecting precursors with appropriate dissolution and decomposition properties.
Contributing Editor: Xiaobo Chen