Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 October 2016
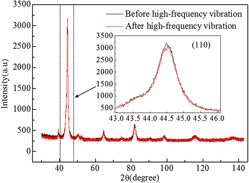
The high-frequency vibration technology was introduced to relieve the quenched residual stress in the Cr12MoV steel based on the high-frequency vibration system that mainly consisted of an electromagnetic vibrator and an amplitude boost unit. The high-frequency vibratory stress relief (VSR) experiments were conducted to study the effectiveness of the high-frequency vibration technology. In addition, the high-frequency vibration plasticity model was developed based on the thermal activation theory to reveal the mechanism of the high-frequency VSR. The results show that the high-frequency VSR has good effects on eliminating residual stress, while the surface hardness for the Cr12MoV steel remains almost the same. Moreover, there are no changes in the grain size of the Cr12MoV steel during the high-frequency VSR, while the dislocation density for the Cr12MoV steel during the high-frequency VSR decreases by 27.21%. The decrease of dislocation density in the Cr12MoV steel is the essence of residual stress relaxation. The findings confirm the significant effects of high-frequency vibration on metal plasticity and provide a basis to understand the underlying mechanism of the high-frequency VSR.