Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 October 2016
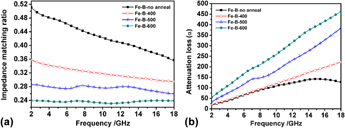
In this paper, Fe–B amorphous submicrometer particles with a size of 180 nm were synthesized by liquid phase reduction method. The as-synthesized Fe–B amorphous submicrometer particles were annealed at 400, 500, and 600 °C, respectively. The effect of annealing temperature on structure, magnetic properties, and microwave absorption properties of Fe–B submicrometer particles was investigated. Results show that the as-synthesized Fe–B amorphous submicrometer particles were crystallized into Fe2B phase when the annealing temperature was 479 °C. The microwave absorption properties of Fe–B submicrometer particles were dependent on annealing temperature, the paraffin composites containing 60 wt% Fe–B submicrometer particles annealed at 500 °C showed a minimal reflection loss (RL) as low as −43.16 dB at 3.12 GHz with a thickness of 5.1 mm, and the effective microwave absorption (RL < −20 dB) was obtained in a wide frequency range of 2.28–10.48 GHz by adjusting the thickness from 1.8 to 6 mm, indicating excellent electromagnetic absorption properties.