Article contents
Diffusion of Cu and interfacial reactions during reflow of Sn–8.5Zn–0.5Ag–0.01Al–0.1Ga alloy on Ni/Cu substrate
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 March 2012
Abstract
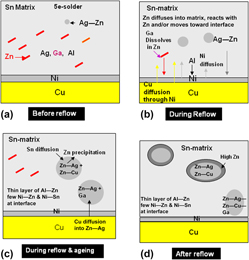
Reflow behavior of a Sn–8.5Zn–0.5Ag–0.01Al–0.1Ga (five-element) solder on the Ni/Cu substrate was investigated under different heating rates. Reflowed samples show decreased Zn and increased AgZn3 in the solder with a reduction in the heating rate. The Zn at the solder/substrate interface was found to be much lower than that in the Sn–Zn solder systems. Cu was observed to be diffused through the electroplated Ni layer and noticed only with the Ag–Zn compound in the solder. Ga was spotted at the interface in the Ag–Zn matrix, whereas Al was detected with the Zn at the interface. Small intermetallic compound (IMC) layer was formed at the interface; however, its amount enhanced with the reduction in the heating rate. Present study relates the reflow behavior of the five-element solder with the reactivity of different elements in the system and its influence on the formation of IMCs in the solder and at the solder/substrate interface.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by


