Article contents
Crystallization properties of IrQ(ppy)2 organometallic complex films
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 May 2017
Abstract
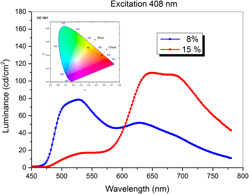
Comparative studies between doped conducting polymers and electrochemical deposited organometallic compounds reveals the interplay between crystalline-amorphous phases with significant contributions to the internal quantum efficiency in the OLED devices. The coexistence of the amorphous and crystalline phase in the electrodeposited film is revealed by the minor micro-crystal products which are present in the amorphous phase in thin films, while the many micro-crystals are randomly distributed in the thick films. Concerning the doped conducting polymers, the level of doping induces crystalline effects as a result of the π–π stacking between molecules, due to the Forester energy transfer processes in which the transfer rate is increased with decreasing of the distances between neighboring molecules. The crystallization processes change the emission properties of the active layers both for the luminance level and all over color, ranging from yellow to red in the case of IrQ(ppy)2 compounds.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Tao Xie
References
REFERENCES
- 5
- Cited by



