Article contents
Catalytic performance and SO2 tolerance of tetragonal-zirconia-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 August 2016
Abstract
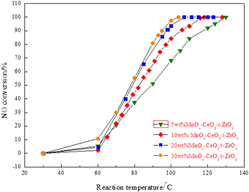
MnOx –CeO2/t-ZrO2 catalyst was prepared by impregnation of nanotetragonal zirconia. The NO conversion of 5 wt% MnOx –CeO2/t-ZrO2 catalyst was 68.1% at 100 °C while that of 30 wt% MnOx –CeO2/t-ZrO2 catalyst was 97.4%. The x-ray diffraction, Brunner–Emmet–Teller measurements (BET), and H2-TPR showed surface properties of the prepared catalysts were good for selective catalytic reduction reactions. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis indicated that Mn4+ and Ce4+ oxidation states were predominant on the surface of the catalyst and so was lattice oxygen which was conducive to Lewis acid sites. NH3-TPD test results demonstrated that Lewis acid sites are predominant on the surface of catalyst. The presence of SO2 reduced the catalyst activity. The realized conversion dramatically decreased to 47% from nearly 100% after 8 h. Characterization of fresh and spent catalysts indicated the deterioration of active component and deposition of NH4HSO4 or (NH4)2SO4 contribute to SO2 poisoning.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by



