Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 July 2020
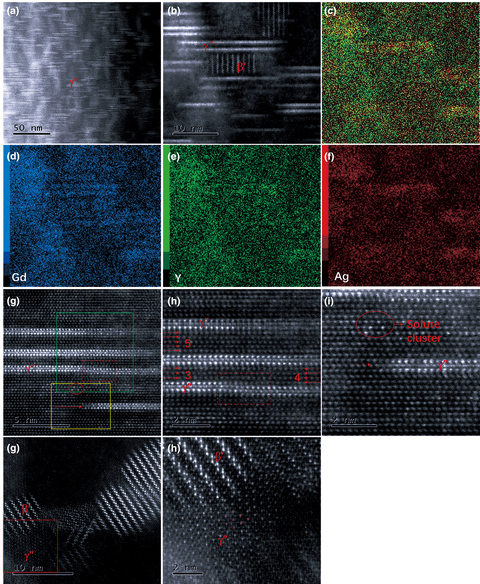
The γ″ phase (hexagonal structure with space group  ${ P\bar{6}}2{ m}$) plays an important role in the strengthening of Mg–Gd–Y–Ag–Zr alloy. In this study, Cs-corrected high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy was applied to characterize the Mg–Gd–Y–Ag–Zr alloy in different conditions (as-cast, solution-treated, and isothermally aged at 200 °C). The nucleation, growing process, and transformation behavior of the plate-shaped γ″ phase were systematically investigated on the atomic scale. We found that the nucleation sites of the γ″ phase were separated by close-packed planes of the Mg matrix and the γ″ phase developed in two perpendicular directions of
${ P\bar{6}}2{ m}$) plays an important role in the strengthening of Mg–Gd–Y–Ag–Zr alloy. In this study, Cs-corrected high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy was applied to characterize the Mg–Gd–Y–Ag–Zr alloy in different conditions (as-cast, solution-treated, and isothermally aged at 200 °C). The nucleation, growing process, and transformation behavior of the plate-shaped γ″ phase were systematically investigated on the atomic scale. We found that the nucleation sites of the γ″ phase were separated by close-packed planes of the Mg matrix and the γ″ phase developed in two perpendicular directions of  $\langle 10\bar{1}0 \rangle$ and ⟨0001⟩. The growing process of the γ″ phase on the atomic scale was captured. The γ″ phase was thermodynamically stable at room temperature, and no transformation behavior of the γ″ phase was observed up to 200 h during isothermal aging at 200 °C.
$\langle 10\bar{1}0 \rangle$ and ⟨0001⟩. The growing process of the γ″ phase on the atomic scale was captured. The γ″ phase was thermodynamically stable at room temperature, and no transformation behavior of the γ″ phase was observed up to 200 h during isothermal aging at 200 °C.