Article contents
An investigation on shape memory behaviors of epoxy resin system
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 June 2015
Abstract
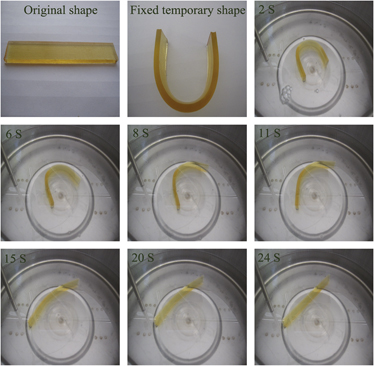
Shape-memory epoxy is receiving considerable attention because of its superior mechanical and thermal properties and excellent shape-memory performance. In this study, a novel series of shape-memory epoxy resins are prepared using hydro-epoxy, hexahydrophthalic anhydride, and diglycidyl 4,5-epoxy tetrahydro phthalate (TDE-85) to further improve the recovery force of shape-memory epoxy resins. The thermal, mechanical, and shape-memory properties of the shape-memory epoxy resin system are investigated by differential scanning calorimetry, dynamic mechanical analysis, bend test, and shape recovery test. Results indicate that the glass transition temperature (Tg), rubber modulus, and room-temperature bend strength increase as TDE-85 content increases. Investigation of the shape-memory behavior of the resin reveals that full recovery can be achieved after only several minutes when the temperature is equal to or above Tg. The shape recovery time decreases with the increase in TDE-85 content at Tg, Tg + 10 °C, and Tg + 20 °C. These results are attributed to the increase in TDE-85 content.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
REFERENCES
- 9
- Cited by


