Article contents
Adsorption of Ni2+ on aminofunctionalized mesoporous silica templated by an anionic surfactant route
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 April 2013
Abstract
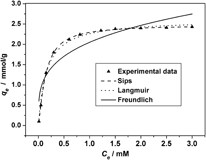
In the present study, aminofunctionalized mesoporous silica (AFMS) was synthesized using the anionic surfactant N-lauroylsarcosine sodium as template and 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane as costructure directing agent. The synthesized mesoporous silica was characterized by the Fourier transform infrared spectra, x-ray diffraction, N2 adsorption-desorption, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy techniques. The application for the removal of Ni2+ from aqueous solution using the synthesized mesoporous silica as adsorbent was investigated. It was found that the solution pH affected adsorption of Ni2+ greatly. The kinetic data of adsorption showed that the removal rate of Ni2+ was substantially high. The adsorption isotherms were fitted using the Sips, Langmuir, and Freundlich models, respectively, and the results showed that the Sips model was the best one to describe the experimental data. From the data of Sips, the maximum adsorption capacity of Ni2+ in respect of the extracted sample is 2.48 mmol/g, much higher than those reported in other literature. The possible adsorption mechanism of Ni2+ on the AFMS was proposed.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 28 , Issue 17: Focus Issue: Advances in the Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties of Bulk Porous Materials , 14 September 2013 , pp. 2325 - 2331
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2013
References
REFERENCES
- 5
- Cited by


