Article contents
Zn2SnO4 coated reduced graphene oxide nanoribbons with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 November 2016
Abstract
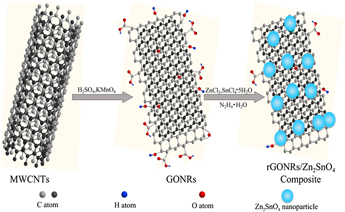
Graphene nanoribbons as a quasi-one-dimensional form of graphene has attracted intensive attention in energy related devices. Upon oxidation and cutting of multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), highly dispersive graphene oxide nanoribbons (GONRs) were obtained, on which Zn2+ and Sn4+ can be homogenously deposited. The reduced graphene oxide nanoribbons (rGONRs)/Zn2SnO4 composite with a homogeneous distribution of nanoparticles on the nanoribbons have been prepared through facile in situ chemical co-reduction process. It is worth noting that the size of Zn2SnO4 particles tightly dispersed on rGONRs is about 15 nm. Benefit from the introduction of rGONRs, the specific surface area and electrode conductivity of rGONRs/Zn2SnO4 can both be effectively enhanced. The as-prepared rGONRs/Zn2SnO4 as anode material for lithium-ion batteries displays desirable electrochemical performance (727.2 mA h/g after 50 cycles at the current density of 100 mA/g), which is mainly attributed to the uniformly distributed Zn2SnO4 nanoparticles and the immobilizing and conducting effects of rGONRs.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by



