Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 June 2011
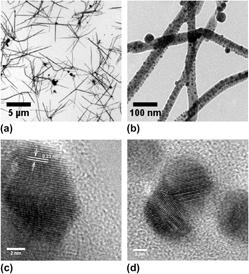
In this work, poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEtOx) is used for synthesis of silver-nanoparticle-embedded polymer nanofibers through a simple polyol process. The factors, such as AgNO3/PEtOx molar ratio R, reaction temperature T, and reaction time t, which would influence the morphology of the nanofiber were studied extensively. Long linear PEtOx nanofibers with length more than 1 μm were obtained under the optimum conditions of R = 5, T = 150 °C, and t = 1 h. PEtOx and reaction temperature were found to be the key factors affecting the final morphology of nanofibers in this system. The physical and chemical properties of these silver-nanoparticle-embedded PEtOx nanofibers were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectrum, x-ray diffraction, and inductive coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. The growth mechanism of the nanofibers is elucidated, and the process is demonstrated to be both kinetically and thermodynamically controlled.