Article contents
Study of layered diamond like carbon and PECVD fluorocarbon films for ultra low dielectric constant interlayer dielectric applications
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 March 2016
Abstract
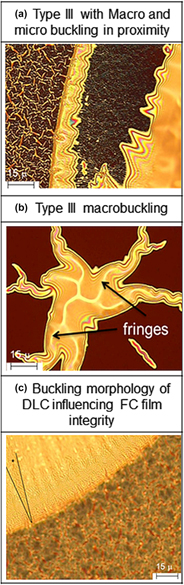
Diamond like carbon (DLC) films deposited using CH4 and Ar and amorphous fluorocarbon (a:C-F) films deposited using CF4 and Si2H6 as precursors were optimized for ultra-low dielectric constant applications by tuning pressure, substrate temperature, and flow rate ratio. Sixty three films belonging to three stack configurations possessed good morphology and adhesion post DLC deposition. Structural and mechanical properties with respect to film integrity, adhesion, roughness, and shrinkage rate were studied. Internal and interface stress distribution results in the increased stability of as deposited DLC–a:C-F–DLC sandwich layers in comparison to a:C-F–DLC stacks. Annealed a:C-F with DLC top coat and As deposited a:C-F are similar in bonding structure. Failure mode is buckling delamination failure with increasing severity in films with higher oxygen incorporation and can be preserved by annealing the fluorocarbon component or providing a DLC base coat. Effect of process parameters on properties relevant to integration has been determined.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 2
- Cited by



