Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 May 2013
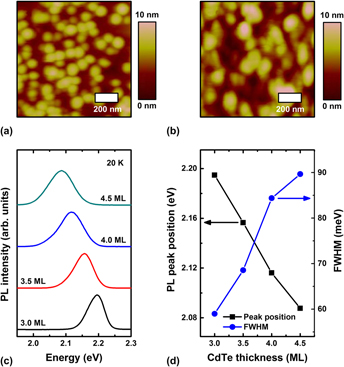
We investigate the size-dependent carrier dynamics and activation energy in cadmium telluride/zinc telluride (CdTe/ZnTe) quantum dots (QDs) grown on silicon (Si) substrates. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra show that the excitonic peak corresponding to transitions from the ground electronic subband to the ground heavy-hole band in CdTe/ZnTe QDs shifts to a lower energy level with increasing CdTe thickness, owing to an increase in the size of the CdTe QDs. Time-resolved PL measurements performed to study the carrier dynamics reveal a longer exciton lifetime for CdTe/ZnTe QDs with increasing CdTe thickness on account of the reduction of the exciton oscillator strength resulting from a strong built-in electric field in the larger QDs. The activation energy of the electrons confined in the CdTe/ZnTe QDs, as obtained from the temperature-dependent PL spectra, increases with increasing CdTe thickness. These results indicate that the carrier dynamics and activation energy of CdTe/ZnTe QDs are affected by the size of the CdTe QDs.