Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 December 2011
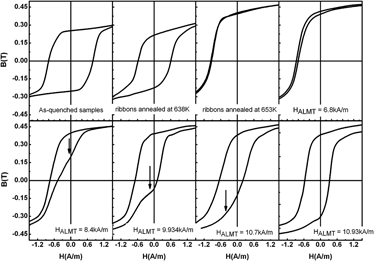
The asymmetrical hysteresis loops of the longitudinal field annealed Co58Fe5Ni10Si11B16 amorphous ribbons were studied. Longitudinal magnetic training was deliberately performed on the annealed samples with exchange bias behavior. It was found that the shifted loops can be technically controlled by training the ribbons to modulate the abnormal magnetic features. The scanning probe microscope results reveal that the AC longitudinal magnetic training can decrease the vertical magnetic signal on the sample surface to a great extent. This skillful magnetic training method provides an approach to tailor the exchange bias behavior in the Co-based amorphous ribbons for potential applications.