Article contents
Improvement of the addition amount and dispersion of hydroxyapatite in the poly(lactic acid) matrix by the compatibilizer-epoxidized soybean oil
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 June 2020
Abstract
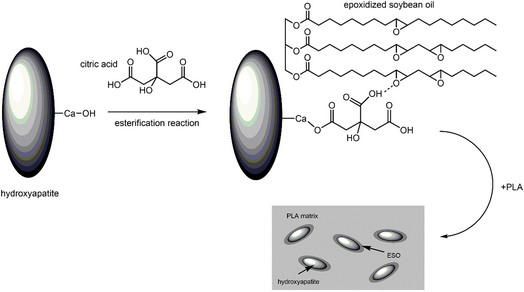
The addition amount and dispersion of inorganic particles into poly(lactic acid) (PLA) still remain a great difficulty, and in the present study, epoxidized soybean oil was used to improve the compatibility between hydroxyapatite (HA) and PLA via the melt blending method. Scanning electron microscopy shows that HA particles can be well dispersed in the PLA matrix when the addition amount is less than 20% in mass, whereas the agglomeration of HA particles and a discrete phase of PLA could be observed when the amount increases to 30%. Therefore, the maximum amount of HA particles can be achieved for the composite with 20% HA which can be also maintaining the bending strength of 71.6 MPa. The osteoblast cells were used to characterize the biocompatibility of the HA/PLA composite, and the results indicate that the number of cells in per unit volume cultured on the HA/PLA composite is 10% higher than that of the PLA. Based on the improved cell biocompatibility and mechanical strength compared to PLA, the composite of HA/PLA prepared in the present study can be served as a potential candidate for the bone fracture repair.
Keywords
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2020
References
- 3
- Cited by



