Article contents
Expandable graphite modification by boric acid
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 February 2012
Abstract
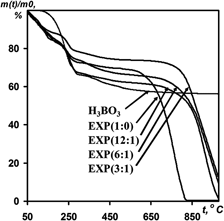
Electrochemical oxidation of graphite in mixed solutions of H2SO4–H3BO3 with various mass ratios was investigated. The potential correction to concentration in the formation of graphite intercalation compound II stage in the system graphite–H2SO4–H3BO3 was determined and compared with other systems. Boric acid was shown not to be co-intercalated with sulfuric acid into graphite matrix, but to be distributed on the surface of expandable graphite (EXP). The amount of boric acid on EXP depends on concentration of H3BO3 in electrolyte and it ranges from 3.7 to 11.0 wt%. Content of boric oxide formed after thermoshocking is equal to 3–9 wt% in exfoliated graphite (EG). Modification resulted in reducing specific surface area of EG. As the pores in modified EG were blocked by boric oxide, the temperature of oxidation of the EG and graphite foil increased by 200 °C.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by


