Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 March 2015
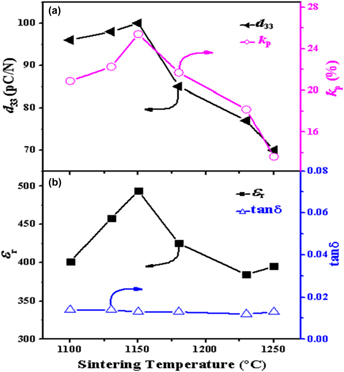
0.7(0.1BiYbO3-0.9PbTiO3)-0.3 Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3 (0.7BYPT-0.3PMN) ternary piezoelectric ceramics were prepared by a columbite precursor method. The effects of sintering temperature on the crystalline phase, microstructure, and electrical properties of the ceramics were systematically investigated. There were two phases coexisting in the 0.7BYPT-0.3PMN ceramics sintered at 1100–1250 °C, one is the perovskite host phase with tetragonal symmetry and the other is Yb2Ti2O7 impurity phase. It was observed that, with increasing sintering temperature, the piezoelectric constant d33, dielectric constant εr, planar electromechanical coupling coefficient kp, and Curie temperature TC increased initially and then decreased. An apparent structure distortion could also be observed in samples synthesized at high sintering temperature due to the severe volatilization of Pb and Bi. The optimum performances of the material were obtained for samples sintered at 1150 °C with d33 = 100 pC/N, εr = 494, kp = 25.4%, and TC = 380 °C, respectively. It can be ascribed to the combined effect of a higher density, structural homogeneity with decreased tetragonality as well as a small amount of pyrochlore phase.